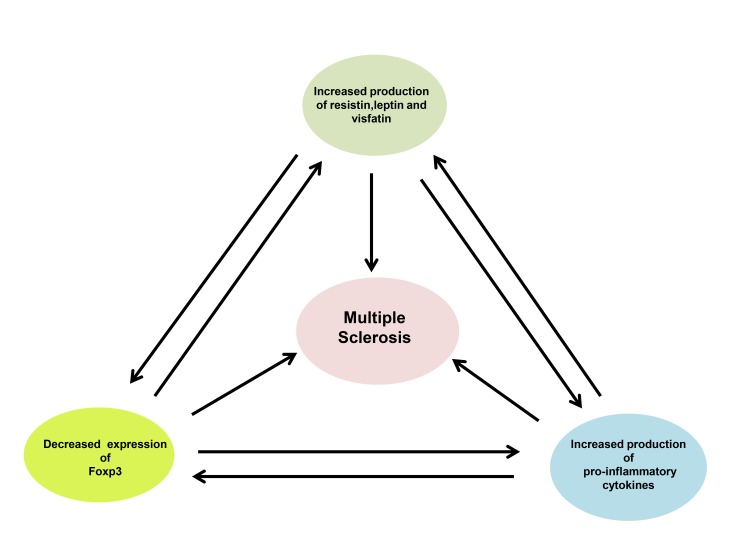
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the proposed mechanism for the pathogenesis of MS.
The elevation of circulating adipocytokines and pro-inflammatory mediators on one hand, and the reduction of FoxP3 expression on the other hand have provided strong evidences into understanding the pathogenesis of MS. Additionally, it is plausible that high level of resistin, visfatin and leptin could enhance pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in a positive feedback loop, which in turn lead to the loss of Foxp3 expression.