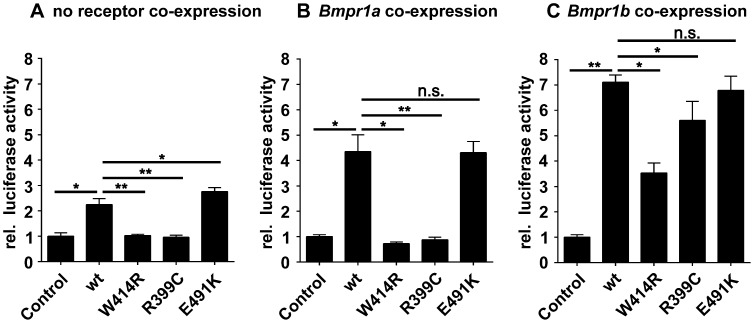
Figure 4. GDF5W414R shows impaired Bmpr1a signaling in a SBE-Luciferase reporter gene assay.
NIH/3T3 cells were transfected with the BMP type I receptors, Bmpr1a or Bmpr1b, as well as with wild type GDF5 and the GDF5 variants GDF5W414R, GDF5R399C and GDF5E491K. As reporter, the SMAD binding element (SBE) was used and firely luciferase was normalized against TK-Renilla luciferase. A: No Bmp type I receptor was co-expressed which resulted in a weak SBE reporter activation for wild type GDF5 and GDF5E491K, whereas in case of GDF5W414R and GDF5R399C signaling activity was absent. B: Bmpr1a co-expression increased the signaling activity of wild type GDF5 and GDF5E491K; however, GDF5W414R and GDF5R399C were not able to induce reporter gene expression. C: Co-expression of Bmpr1b further increased the signaling activity of wild type GDF5 and GDF5E491K compared to co-expression with Bmpr1a. In case of GDF5W414R and GDF5R399C, Bmpr1b co-expression rescued their signaling activity. The means of triplicate measurements are shown, error bars indicate standard deviation and a represent experiment is shown. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student's t test (n.s.: not significant; *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01). Significances are related to the respective wild type GDF5 value.