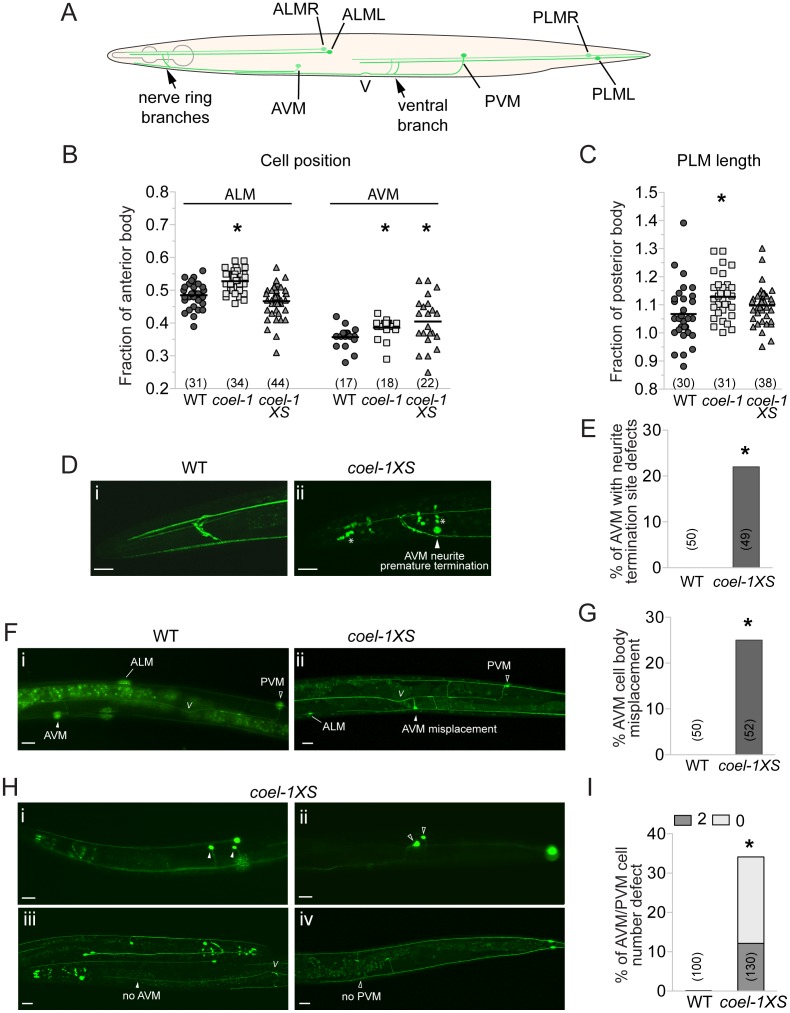
Figure 4. Touch receptor neuron (TRN) morphology, position and number defects in the coel-1 overexpression and deletion strains.
A. Schematic representation of wild-type morphology of the 6 mechanosensory neurons of C. elegans. B. ALM and AVM cell bodies are misplaced posteriorly in coel-1 mutants compared to wild-type animals. Only AVM cell bodies are misplaced in coel-1XS animals. Each data point represents the distance from each cell body to the back of the pharynx divided by the length of the anterior body, (i.e., from the tip of the nose to the vulva). C. PLM neurites in coel-1 mutants are statistically significantly longer than in wild-type. Values indicated represent the length of each PLM neurite divided by the length of the posterior body (i.e., from the vulva to the tail). In panels B and C, the horizontal bar corresponds to the mean of all data points. D. Typical anterior neurite termination site in wild-type worms expressing zdIs5 (mec-4::GFP), a TRN-specific reporter. (i) example of AVM neurite premature termination (arrowhead) at the nerve ring observed in coel-1XS animals; (ii) asterisks show crosstalk into the GFP channel from dpy-30::dsRED, a co-marker used for the coel-1 overexpression strain. E. Quantitative analysis of the AVM termination site defect in animals overexpressing coel-1. F. In wild-type animals, one AVM and one PVM are observed and AVM is localized anterior to ALM cell bodies. (i) example of AVM mispositioning in coel-1XS animals, where AVM is found posterior to the vulva; (ii) Quantification of AVM position defect is presented in G. H. AVM/PVM cell number defect in coel-1XS animals. Images shown are of animals with two cells or no cell in AVM (i, iii) and/or PVM (ii, iv); positions are shown and the quantification is reported in I. Scale bar represents 20 µm. V, vulva; WT, wild-type. Brackets indicate the number of neurons measured or scored. *, p≤0.05, Fisher exact test.