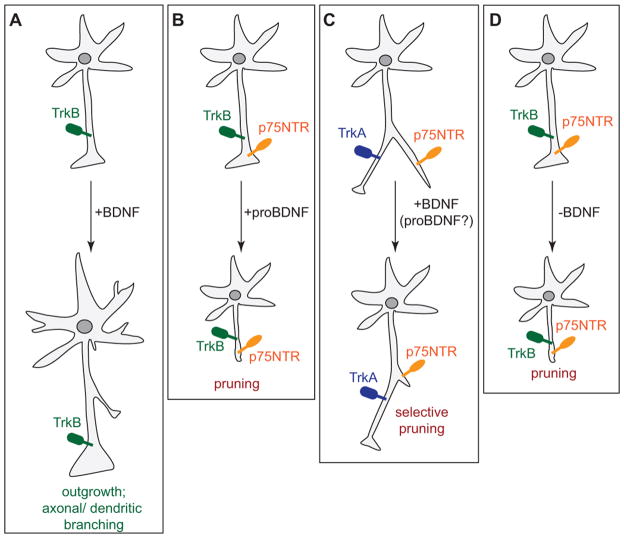
Fig. 2. Different modes of BDNF action on neuronal growth.
(A) BDNF signals through TrkB to enhance axonal and dendritic growth and arborisation. (B) The BDNF precursor proBDNF has an opposing effect. It signals through p75NTR to decrease neurite outgrowth and initiate growth cone collapse. (C) In absence of TrkB, BDNF activates p75NTR to induce axonal pruning. (D) Sudden withdrawal of BDNF not only stops enhancing outgrowth, but also leads to dying back of axons.