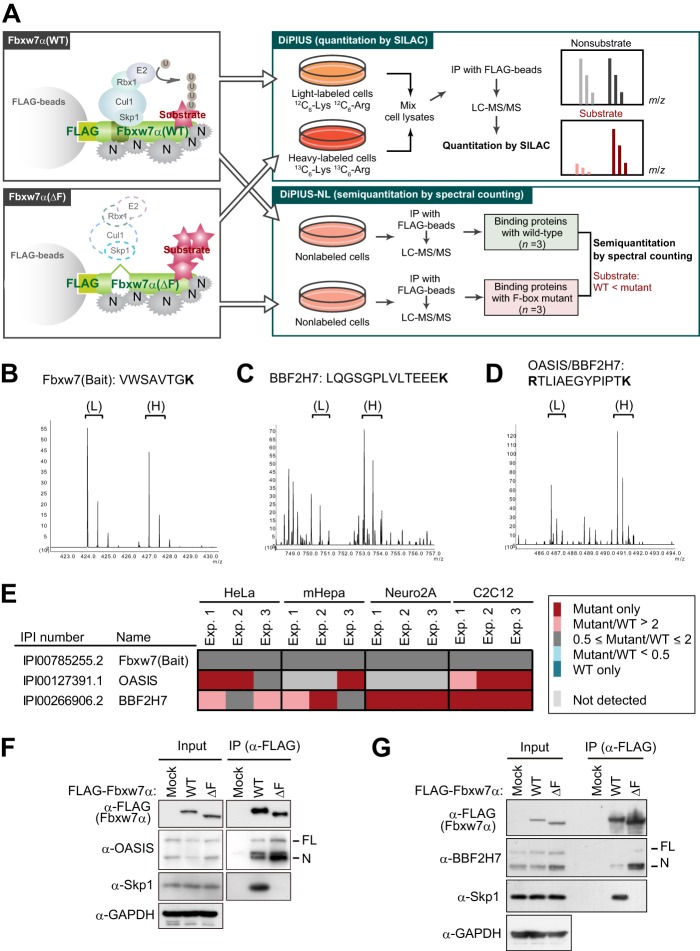
FIGURE 1.
Identification of OASIS and BBF2H7 as candidate substrates of SCFFbxw7 by DiPIUS analyses. A, strategy for comprehensive identification of substrates for Fbxw7α. Schematics of DiPIUS and DiPIUS-NL are shown. Proteins that bind to WT or ΔF mutant forms of Fbxw7α are analyzed by quantitative SILAC (DiPIUS) or semiquantitative spectral counting (DiPIUS-NL). U, ubiquitin; N, nonspecific binding protein; IP, immunoprecipitation. B–D, representative mass spectra for DiPIUS analysis of Fbxw7α in mCAT-HeLa cells subjected to SILAC. Peak areas of light (L) and heavy (H) tryptic peptides derived from Fbxw7 (bait) (B), BBF2H7 (C), or OASIS and BBF2H7 (D) represent the abundance of proteins associated with the WT or ΔF mutant forms of Fbxw7α. E, OASIS and BBF2H7 were detected by DiPIUS-NL in mCAT-HeLa, mHepa, Neuro2A, or C2C12 cells. The ratios of the number of spectral counts for WT and mutant F-box proteins are indicated by the color scale. Proteins with a mutant/WT ratio of > 2 in at least two of three independent experiments (Exp.) were considered binding proteins with a higher affinity for the mutant F-box protein than for the WT protein. F and G, coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous OASIS (F) and BBF2H7 (G) as well as of Skp1 with FLAG-tagged WT or ΔF mutant forms of Fbxw7α from mCAT-HeLa cell lysates. Immunoprecipitates (IP) prepared with antibodies to FLAG from cells expressing the recombinant Fbxw7α proteins (or from those transfected with the corresponding empty vector, Mock) and treated with 10 μm MG132 for 6 h were subjected, together with the original cell lysates (Input), to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies (α-).