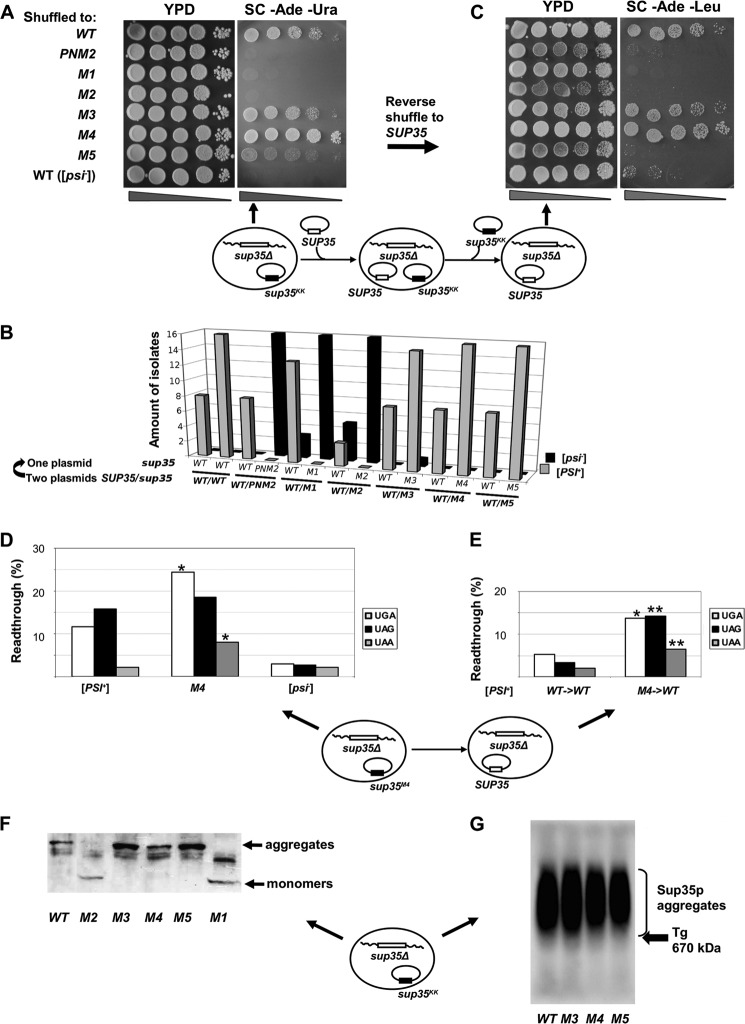
FIGURE 3.
sup35KK alleles have the opposite effect on [PSI+] phenotype in the absence of wild type SUP35. A, five serial dilutions of 10-7A-D832 (sup35Δ) derivatives containing the pRSU1 plasmid with wild type or mutant alleles of SUP35. B, amount of [PSI+] and [psi−] isolates after the loss of one of the plasmids. C, isolates shown on panel A were retransformed with pRSU2 (SUP35 (WT)) with subsequent loss of the pRSU1 plasmid, one representative clone from 16 tested in each case is shown. In both panels A and C one representative transformant was spotted onto YPD and SC-Ade. Derivatives of 7A-D832 (sup35Δ [psi−]) containing the corresponding plasmids with a wild type copy of SUP35 were used as a negative control in panels A–C. Schematic representation of the plasmid shuffling assay is shown under panels A and C. Arrows indicate where the corresponding phenotype is demonstrated. D and E, read through efficiency in [PSI+] 10-7A-D832 derivatives bearing sup35-M4 mutation after direct (C) and reverse (D) shuffle measured by in vivo β-galactosidase activity assay. The efficiency of suppression was calculated as a ratio of β-galactosidase activity in cells harboring lacZ with premature termination codon to lacZ (WT) control. The results are from at least three separate experiments. Significant differences from wild type [PSI+] are shown by one or two asterisks (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively). F, SDS-PAGE with additional boiling of [PSI+] aggregates in 10-7A-D832 (sup35Δ) derivatives containing the pRSU1 plasmid with wild type SUP35 or sup35KK. The captions below the lanes indicate the sup35 allele. A schematic representation of the plasmid combination is shown near the panel. G, SDD-AGE analysis of Sup35p aggregates in transformants shown in panel A. The arrow marks the position of thyroglobulin (Tg, 670 kDa) in gel revealed by Coomassie staining.