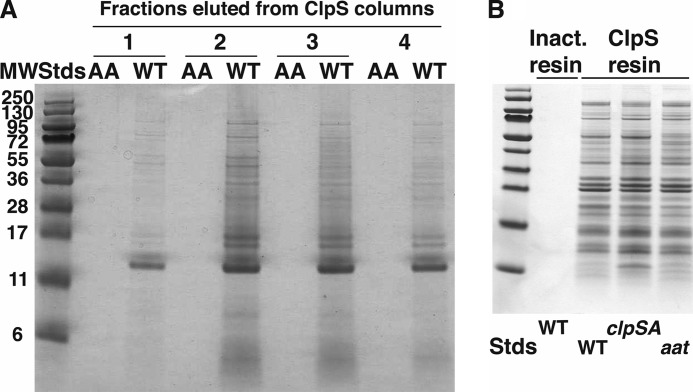
FIGURE 2.
Differential capture of E. coli cell proteins on a wild-type ClpS affinity column. A, many E. coli proteins bind to wild-type ClpS and not to ClpSDD/AA. Affinity resins were prepared with either wild-type ClpS or mutated ClpS in which Asp35 and Asp36 were changed to alanine. Extracts of cells harvested during stationary phase were clarified, and equal portions were loaded onto columns (1-ml bed volume) with either wild-type or mutated ClpS. The columns were washed with several column volumes of buffer, and proteins were eluted with buffer containing 1 mm FKTA-NH2. Fractions of 0.5 ml were collected, and equal aliquots of four fractions that contained protein eluted from the wild-type column were mixed with SDS sample buffer and loaded onto an SDS-polyacrylamide gel (lanes labeled WT). Parallel fractions from the ClpSDD/AA were loaded in adjacent lanes as indicated (lanes labeled AA). Proteins were detected by staining with Coomassie Blue. B, pulldown of proteins from E. coli cells carrying mutations in the N-end rule pathway. Clarified cell lysates from wild-type, ΔclpSA, or Δaat strains were loaded onto a ClpS affinity column, and bound proteins were eluted with FKTA. No proteins were detected in the FKTA eluate when wild-type lysates were applied to a control column with inactivated (Inact.) resin that had no cross-linked ClpS. Stds, standards.