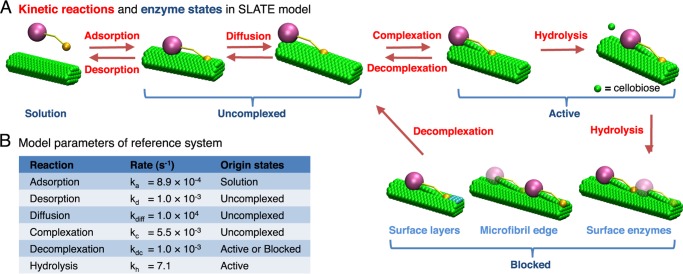
FIGURE 1.
Illustration of the SLATE model for TrCel7A. A, kinetic reactions (labeled in red) and enzyme states (labeled in blue) in the SLATE model. Cellulase enzymes can participate in one of the following reactions: adsorption, desorption, diffusion, complexation, decomplexation, and hydrolysis. Only hydrolysis is treated as an irreversible reaction. With these reaction steps, an enzyme can be in one of the four states: solution, uncomplexed, active, and blocked. These states are mutually exclusive and completely exhaustive. A blocked enzyme can be stalled by uneven surface layers, the nonreducing edge of the microfibril substrate, or the other surface enzymes. B, kinetic rates for the reference system. The possible originating states for each reaction is shown under Origin states.