FIGURE 1.
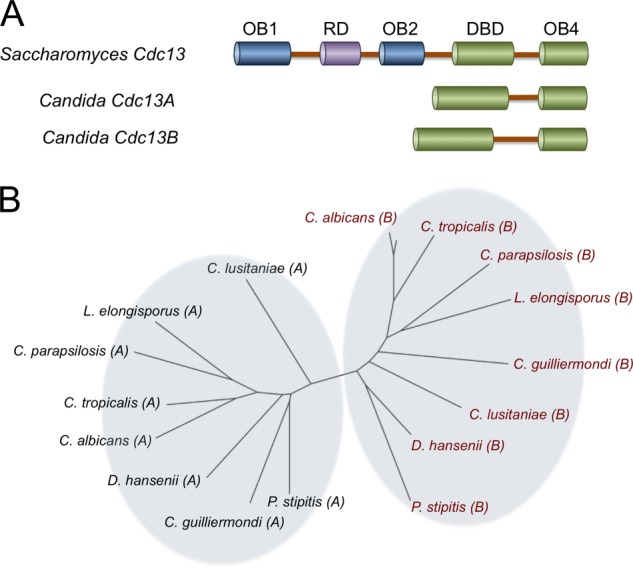
The domain organization and phylogenetic relationship of Cdc13 homologues in Saccharomycotina. A, the domain organizations of Cdc13, Cdc13A, and Cdc13B proteins from Saccharomyces and Candida species are illustrated. B, the relationship between the Candida Cdc13A and Cdc13B family members was analyzed using the neighbor-joining method, and the results were plotted using FigTree. The Cdc13A and Cdc13B family members are designated by A and B in parentheses following the species names. The accession codes for the Cdc13A members are as follows: Debaryomyces hansenii, XP_461188; C. albicans, XP_719034; Candida parapsilosis, CPAG_03609; Lodderomyces elongisporus, XP_001526643; C. guilliermondii, XP_001486879, PGUG_00256; C. lusitaniae, CLUG_03319; C. tropicalis, CTRG_04305; and P. stipitis, XP_001384972. The accession codes for the Cdc13B members are as follows: D. hansenii, DEHA0F12859g; C. albicans, CAWG_05171; C. parapsilosis, CPAG_02733; L. elongisporus, LELG_04784.1; C. guilliermondii, PGUG_00873; C. lusitaniae, CLUG_05491.1; C. tropicalis, CTRG_02892; and P. stipitis, XP_001384748.
