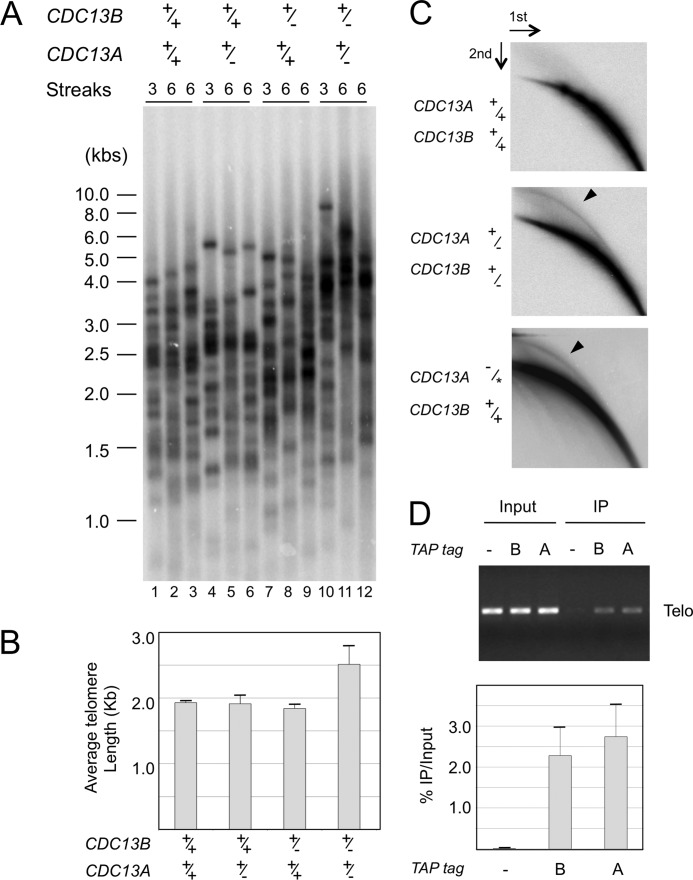
FIGURE 2.
The role of Cdc13B in telomere regulation. A, the indicated strains were passaged in YPD and their telomeres subjected to Southern analysis. B, the average telomere lengths ± S.D. in the indicated strains were determined from three independent transformants after six streaks and plotted. C, the levels of t-circles in the wild type, a compound heterozygous, and a CDC13A-TAP strain (18) were assayed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and Southern analysis. The TAP-tagged allele of Cdc13A is designated by an asterisk. The percentages of total telomere hybridization signals in the circular DNA arcs (marked by arrowheads in two blots) are 0.4, 2.0, and 2.3%, respectively. D, the wild type (−) and two TAP-tagged strains (one carrying just one copy of CDC13A-TAP (lane A) and the other carrying one copy of CDC13B-TAP (lane B)) were subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis. The levels of telomeric DNA in 2% of the Input and 20% of the immunoprecipitation (IP) samples were estimated by PCR amplification of a subtelomeric fragment on chromosome 3. A representative assay is shown at the top, and the calculated percentages of telomeric DNA trapped in the immunoprecipitation samples are plotted at the bottom. Data (average ± S.D.) are from three independent experiments.