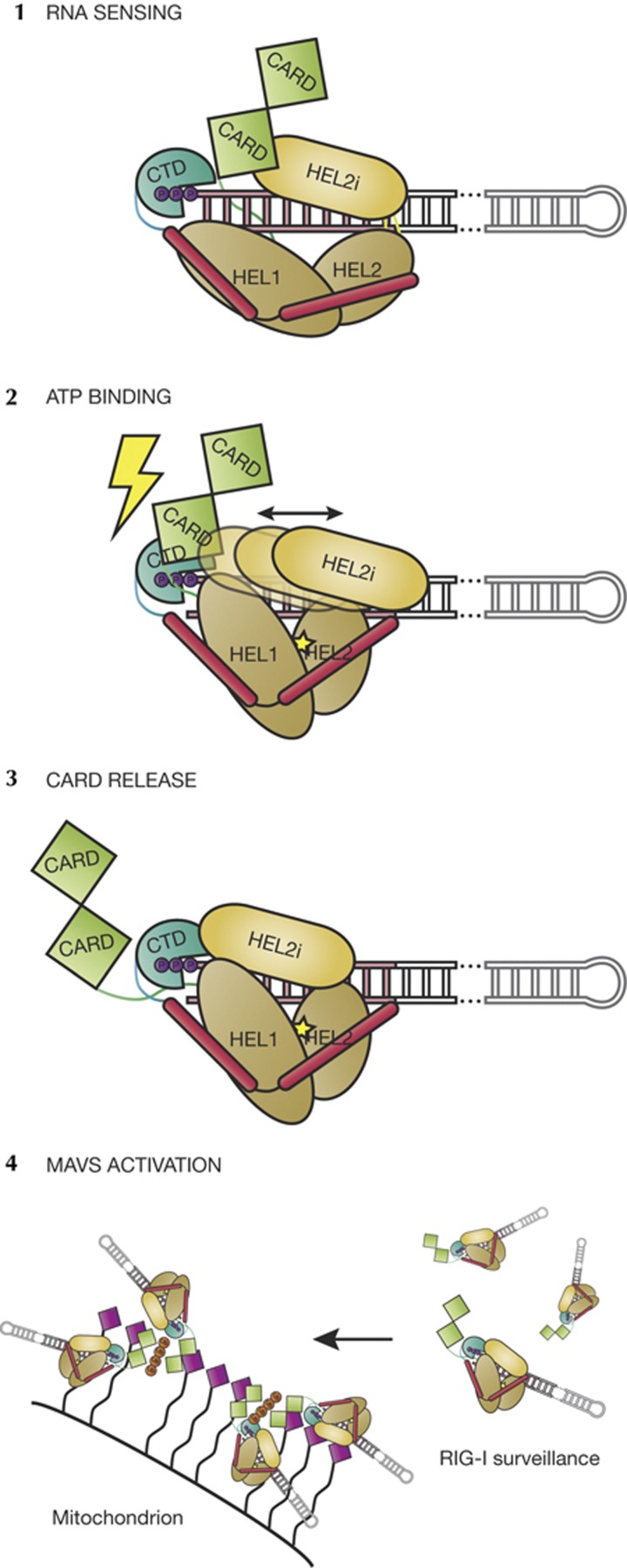
Figure 5.
Model of RIG-I activation. (1) RNA binding is the first trigger of the RIG-I-mediated interferon response. The CTD binds firmly to the 5′ end of the duplex RNA. The CARD domains rest on the HEL2i domain [17] and likely are not displaced upon RNA binding. (2) ATP binding serves as the second trigger, whereupon HEL1 and HEL2 close and HEL2 initiates contacts with the tracking strand, creating a clash between the CTD and the CARDs [12]. HEL2i scanning might be directly linked to ATP binding and hydrolysis, or it might move stochastically. (3) Once the CARD domains are released, a 1:1:1 RIG-I:RNA:ATP ternary complex is competent for signalling and activation of MAVS. (4) Ubiquitin-mediated multimerization (tetraubiquitin shown in orange) of RIG-I through the CARD domains might be required for MAVS activation [15, 30]. CARD, caspase activation and recruitment domain; CTD, carboxy-terminal domain; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene-I.