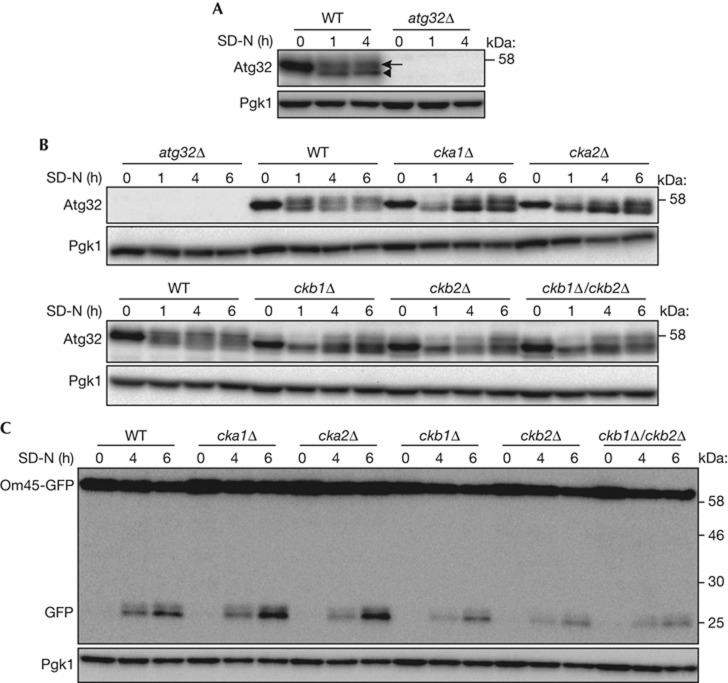
Figure 1.
Deletion of CK2 components affects Atg32 phosphorylation. (A,B) WT and atg32Δ strains were cultured in YPL medium until the mid-log growth phase and then shifted to SD-N medium for 0, 1, or 4 h (A). WT, atg32Δ, cka1Δ, cka2Δ, ckb1Δ, ckb2Δ, and ckb1Δ/ckb2Δ strains were cultured in YPL medium until the mid-log growth phase, and then shifted to SD-N medium for 0, 1, 4 or 6 h (B). The phosphorylation status of Atg32 was observed by immunoblotting with anti-Atg32 and anti-Pgk1 (loading control) antibodies. The arrowhead and arrow indicate dephosphorylated and phosphorylated Atg32, respectively. (C) WT, atg32Δ, cka1Δ, cka2Δ, ckb1Δ, ckb2Δ and ckb1Δ/ckb2Δ strains expressing Om45-GFP were cultured in YPL medium until the mid-log growth phase and then shifted to SD-N for 0, 4 or 6 h. GFP processing was monitored by immunoblotting with anti-GFP and anti-Pgk1 antibodies. CK2, Casein kinase 2; GFP, green fluorescent protein; WT, wild type.