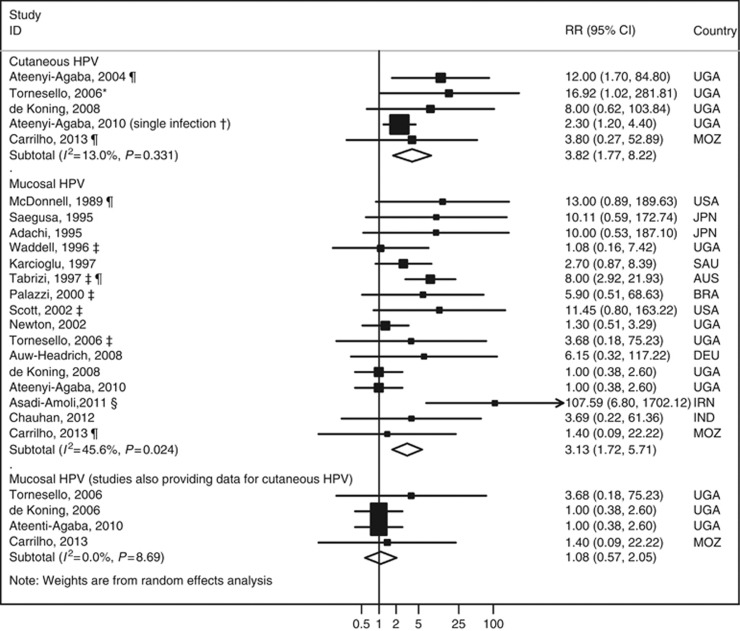
Figure 3.
Meta-analyses of the studies assessing the relation between infection with cutaneous and mucosal human papillomavirus (HPV) subtypes and OSSN. * indicates that this RR estimate was computed by the authors of the present meta-analysis with data provided in the original report, although the controls were frequency age- and sex-matched with the cases; a sensitivity analysis excluding this study yielded virtually the same results (RR=3.10, 95% CI: 1.59–6.03, I2=5.0%). † indicates that from this study RR estimates were available both for multiple and single infection, and the latter was selected for meta-analysis because it was more common than multiple infections (among the HPV-infected, 54.5% were infected with a single type and the remaining with multiple); in a sensitivity analysis including the estimate for multiple infection (OR=18.3, 95% CI: 6.2–54.4), the overall RR estimate was 13.44 (95% CI: 5.99–30.15, I2=0.0%). ‡ indicates that the RR estimates were computed by the authors of the present meta-analysis with data provided in the original report, although these five studies were matched case–control studies; the overall RR estimate is 2.58 (95% CI: 1.28–5.16, I2=44.7%) if these studies are excluded. § indicates that excluding this study, the summary RR estimate was 2.55 (95% CI: 1.51–4.29, I2=30.5%). ¶ indicates these studies include >10% of the subjects in the control group with pterygia or pinguecula. When excluding them from the analysis, the overall RR estimate was 3.52 (95% CI: 1.23–10.08, I2=21.8%) and 2.50 (95% CI: 1.35–4.65) for the association between cutaneous and mucosal HPV and OSSN, respectively. Abbreviations: AUS=Australia; BRA=Brazil; DEU=Germany; IND=India; IRN=Iran; JPN=Japan; MOZ=Mozambique; RR=relative risk; SAU=Saudi Arabia; UGA=Uganda; USA=United States of America.