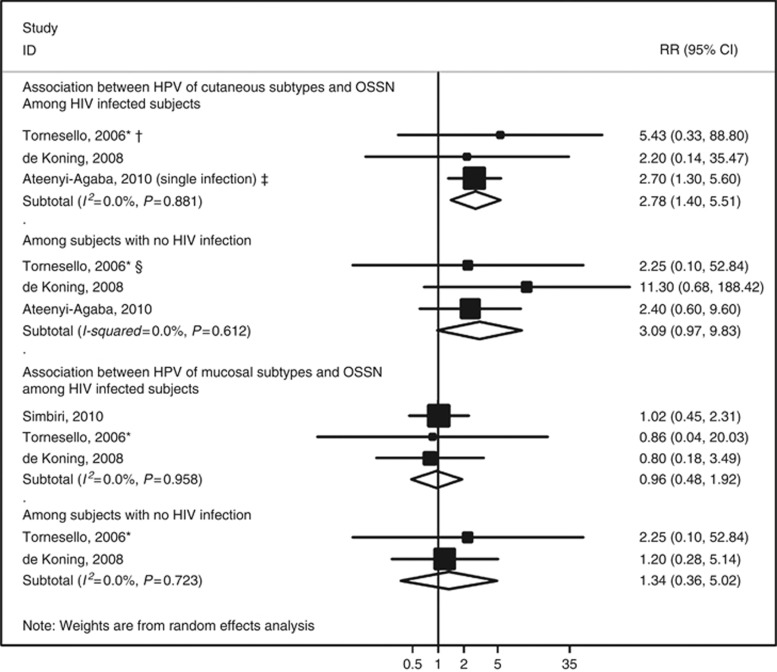
Figure 4.
Meta-analyses of the studies addressing the association between human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) by HIV status. * indicates that this RR estimate was computed by the authors of the present meta-analysis with data provided in the original report, although the controls were frequency age- and sex-matched with the cases; † indicates that a sensitivity analysis excluding this study yielded an overall RR of 2.66 (95% CI: 1.33–5.40, I2=0.0%); ‡ indicates that from this study RR estimates are available both for multiple and single infection, and the latter was selected for meta-analysis because it was more common than multiple infections (among the HPV-infected, 54.5% were infected with a single type and the remaining with multiple); in a sensitivity analysis including the estimate for multiple infection (OR=15.4, 95% CI: 5.2–45.4), the overall relative RR estimate was 11.87 (95% CI: 5.13–27.46, I2=6.9%); § indicates that a sensitivity analysis excluding this study yielded an overall RR of 3.25 (95% CI: 0.94–11.27, I2=0.0%). Abbreviation: RR=relative risk.