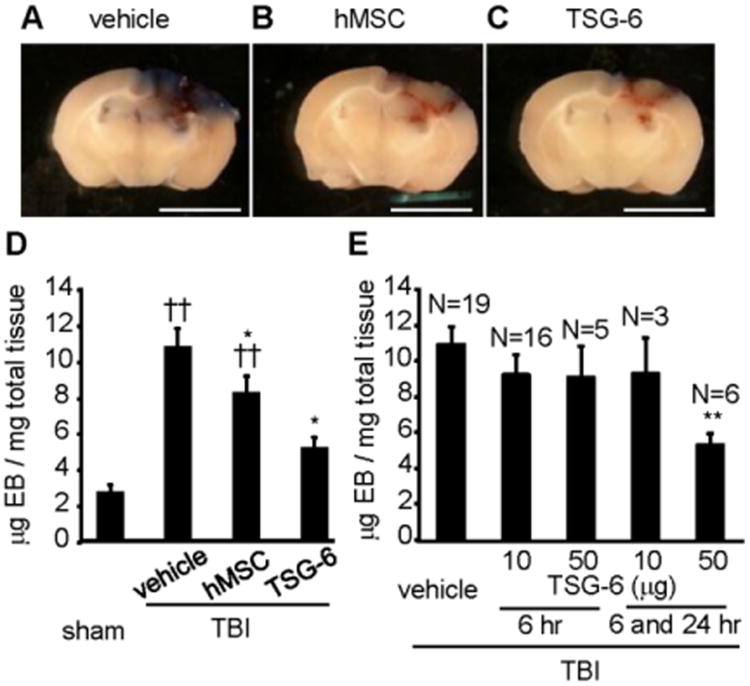
Fig. 4.
IV-injected hMSCs or TSG-6 protein decreased blood brain barrier (BBB) permeability in mice 3 days after TBI. hMSCs (106 cells/mouse) were administrated 6 hour after TBI. TSG-6 protein at a dose of 50 μg/mouse was administered twice at 6 and 24 hour after TBI (A-D). In assay (E), TSG-6 was administrated at 10 or 50 μg/mouse dose once or twice. (A-C) Representative brain slices of the site of cortical contusion injury after administration of vehicle (A), hMSCs (B) or TSG-6 (C) and recovered 3 days post TBI. Blue represents Evans Blue dye extravasation at the site of injury. Scale bars = 5 mm. (D) Quantitative data of Evans blue level in the ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere tissue of mice from sham operated group (n=8) and injured group treated vehicle (n=21), hMSCs (n=14) or TSG-6 (n=6) at 3 days after CCI. hMSCs (106 cells/mouse) were administrated 6 hour after TBI. TSG-6 protein at a dose of 50 μg/mouse was administered twice at 6 and 24 hour after TBI. (E) Dose-dependency and time window of TSG-6 treatment in BBB breakdown following TBI. Numbers of samples are indicated above the columns. Evans Blue dye was extracted from brain at 3 days after CCI. All data are represented as mean ± SEM. ††p < 0.01 versus the sham group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus the vehicle group.