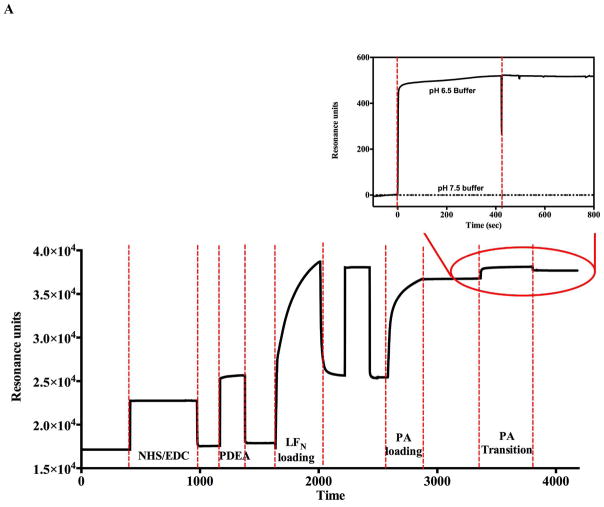
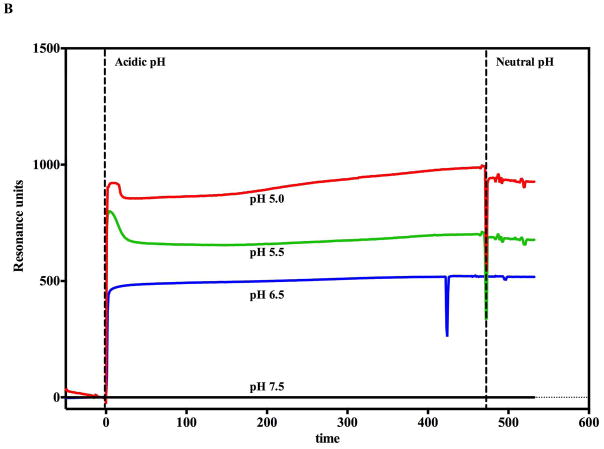
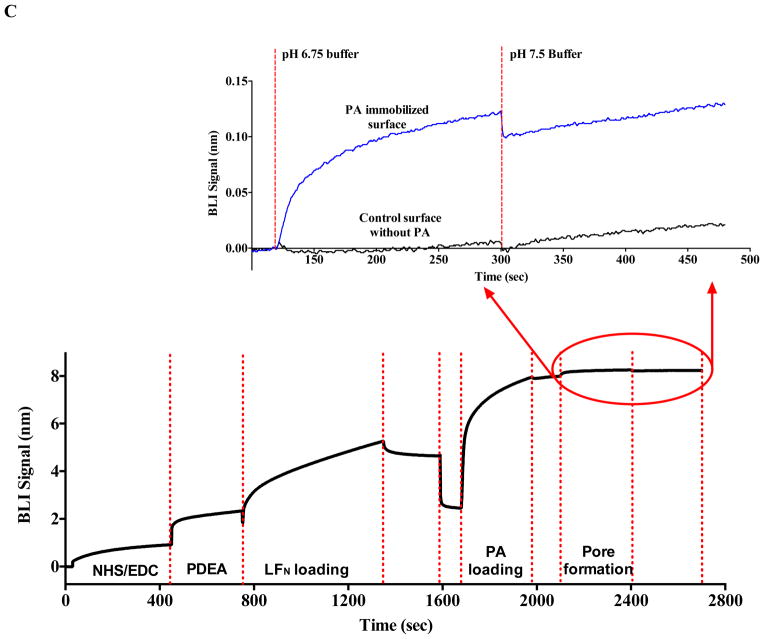
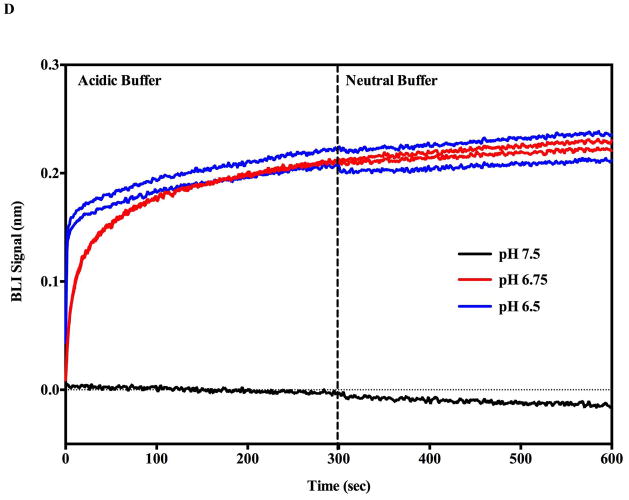
Figure 2.
Monitoring the PA prepore acid induced transition in realtime by SPR Biacore 3000 (A and B) and BLI Octet system (C and D). Complete sensorgrams for SPR (A) and BLI (C) as observed for pH jumps. Highlighted regions in A and C show the comparative amplitudes of the pH induced changes for each label free platform. The PA was immobilized on the biosensors and initially treated with buffers of varying acidic pH followed by increasing the pH back to neutral. The pH induced signal changes remain once the buffer is returned to neutral pH, indicating that the origin of the signal change was irreversible. As the pH jumps approach late endosomal pH conditions (pH 5.5 to 5.0), the kinetic transitions become more rapid for both SPR (B) and BLI (D) (rates listed in Table 1, kinetic fits to both Octet BLI and single channel BLI (BLItz) data in Supplemental Figure 2). Uncorrected single channel BLI data shown in supplemental Figure 1.