Table 1.
Parameters and equations of a collision-based analysis, plus dimensionless speed and individual limbs cost of transport.
| force vector (N), F | 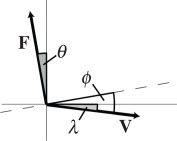 |
|
| velocity vector (ms−1), V | ||
| instantaneous angles (radians): θ denotes force, λ denotes velocity and ϕ denotes collision | ||
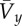 is mean forward velocity; h is hip height; g is acceleration of gravity on the Earth; x is a multiplier of gravity; n is the number of samples in the stride period; m is body mass is mean forward velocity; h is hip height; g is acceleration of gravity on the Earth; x is a multiplier of gravity; n is the number of samples in the stride period; m is body mass | ||
| dimensionless speed (the square root of Froude number) | 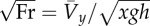 |
equation (1.1) |
| instantaneous force angle, where unit vector a is normal to the substrate and upward | 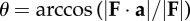 |
equation (1.2) |
| force angle determined by force-averaging over the contact periods of the stride | 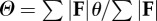 |
equation (1.3) |
| instantaneous velocity angle, where unit vector b is parallel to the substrate and in the direction of travel | 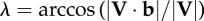 |
equation (1.4) |
| velocity angle determined by velocity-averaging over the contact periods of the stride | 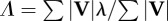 |
equation (1.5) |
instantaneous collision angle determined from the dot product of force on velocity—the arcsine rotates this angle by π/2 such that it quantifies the deviation from 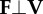
|
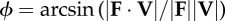 |
equation (1.6) |
| collision angle determined by force- and velocity-averaging over the contact periods of the stride | 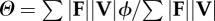 |
equation (1.7) |
mechanical cost of motion is a normalized absolute value of CoM power equivalent to Φ when 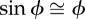 ; the small angle approximation of equation (1.6) is substituted into equation (1.7) ; the small angle approximation of equation (1.6) is substituted into equation (1.7) |
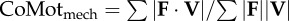 |
equation (1.8) |
| for small vertical and lateral oscillations | 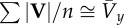 |
equation (1.9) |
| for small fore–aft and lateral forces | 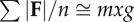 |
equation (1.10) |
individual limbs cost of transport is a normalization of the absolute value of individual limb power [20], where 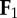 and and 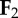 indicate the force vectors of each limb indicate the force vectors of each limb |
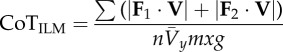 |
equation (1.11) |
mechanical cost of transport is a normalized absolute value of CoM power equivalent to  when the conditions of equations (1.9) and (1.10) are met when the conditions of equations (1.9) and (1.10) are met |
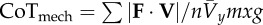 |
equation (1.12) |
| impulse angle for the stride, where I is the impulse vector and unit vector a is normal to the substrate and upward | 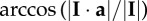 |
equation (1.13) |
| collision fraction determined by force- and velocity-averaging over the contact periods of the stride | 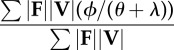 |
equation (1.14) |
