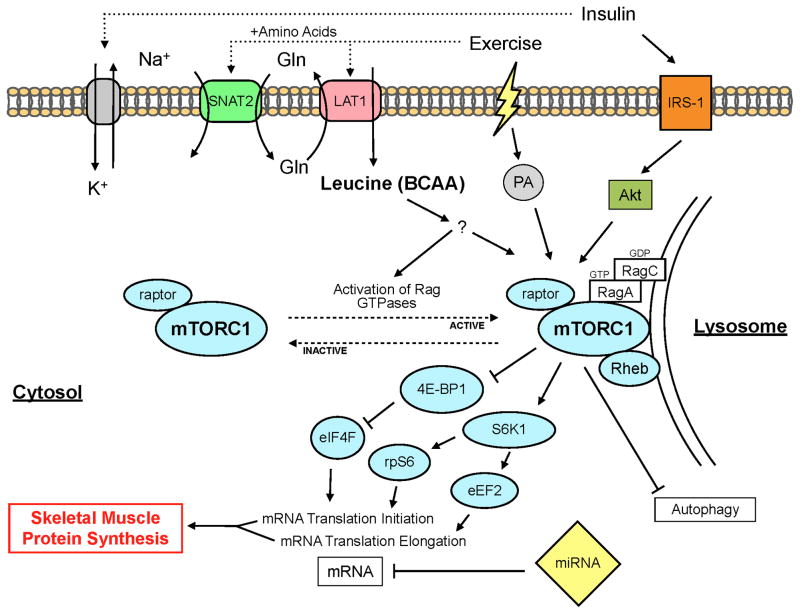
Figure 1.
Simplified schematic of the proposed cellular mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle protein synthesis in response to amino acids, insulin, and exercise. 4E-BP1, 4E binding protein 1; Akt, protein kinase B; BCAA, branch chain amino acids; eEF2, eukaryotic elongation factor 2; eIF4F, eukaryotic initiation factor 4F; Gln, glutamine; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1; LAT1, L-type amino acid transporter 1; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; PA, phosphatidic acid; Rag, Ras-related GTPase; rpS6, ribosomal protein S6; S6K1, p70 ribosomal S6 kinase 1; SNAT2, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 2