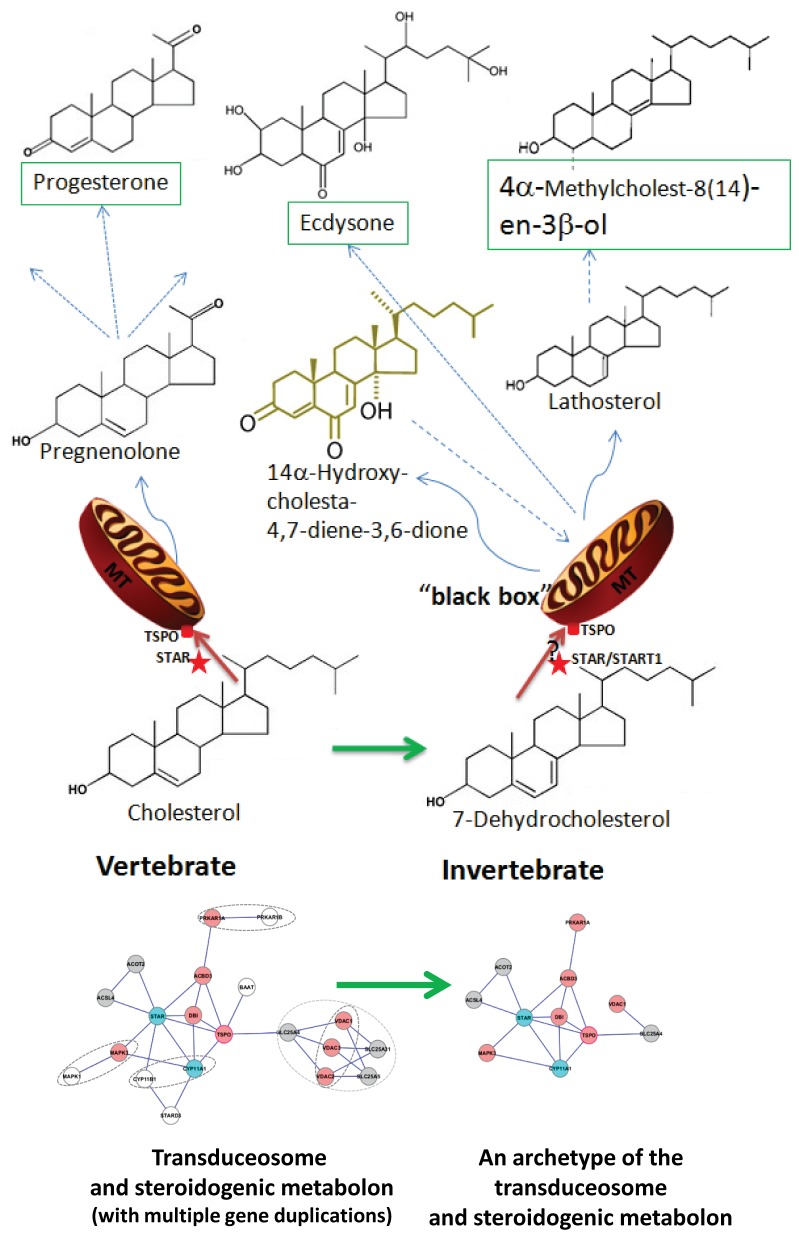
Figure 9. A diagram of the complex of evolutionary steroidogenesis in animals.
The main players in the complex, TSPO and STAR, are indicated on the surface of mitochondria. Precursors (cholesterol for vertebrates and 7-dehydrocholesterol for invertebrates), and first metabolites (pregnenolone for human and lathosterol for worms), intermediate metabolites (progesterone), and/or final products (ecdysone for insects) are indicated. The “black box” refers to the initial steps of steroidogenesis in insects as the enzymes in this process are unknown [100]. The predicted functional interaction networks of the proteins involved in the complex was generated using version 9.0 of the STRING database [101]. The dotted oval circles indicate the gene duplication event. Red indicates the gene is conserved from mammals to invertebrates, light blue indicates genes with sequence divergence but with similar biological function, grey indicates genes with divergence in both sequence and function, and white indicates that the duplicated gene may not be involved in the complex.