Figure 7. The homologous-pairing activities of the RAD51A1(A2L2) and RAD51A2(A1L2) mutants.
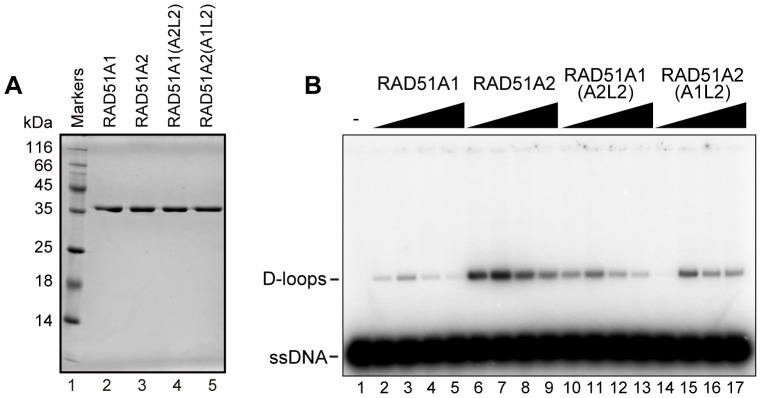
(A) Purified RAD51A1(A2L2) and RAD51A2(A1L2) mutants. Lane 1 indicates the molecular mass markers, and lanes 2 and 3 represent RAD51A1 and RAD51A2, respectively. Lanes 4 and 5 represent RAD51A1(A2L2) and RAD51A2(A1L2). An aliquot (0.5 µg) of each protein was analyzed. (B) The D-loop formation assay (Protein titration experiments). The indicated amounts of rice RAD51A1, RAD51A2, RAD51A1(A2L2), or RAD51A2(A1L2) were incubated with the 32P-labeled 50-mer ssDNA, and the homologous-pairing reaction was initiated by the addition of superhelical dsDNA. Reactions were allowed to proceed for 5 min. Lane 1 indicates a negative control experiment without protein, and lanes 2–5, 6–9, 10–13, and 14–17 represent the reactions conducted with RAD51A1, RAD51A2, RAD51A1(A2L2), and RAD51A2(A1L2), respectively. The protein concentrations were 0.4 µM (lanes 2, 6, 10, and 14), 0.6 µM (lanes 3, 7, 11, and 15), 0.9 µM (lanes 4, 8, 12, and 16), and 1.2 µM (lanes 5, 9, 13, and 17).
