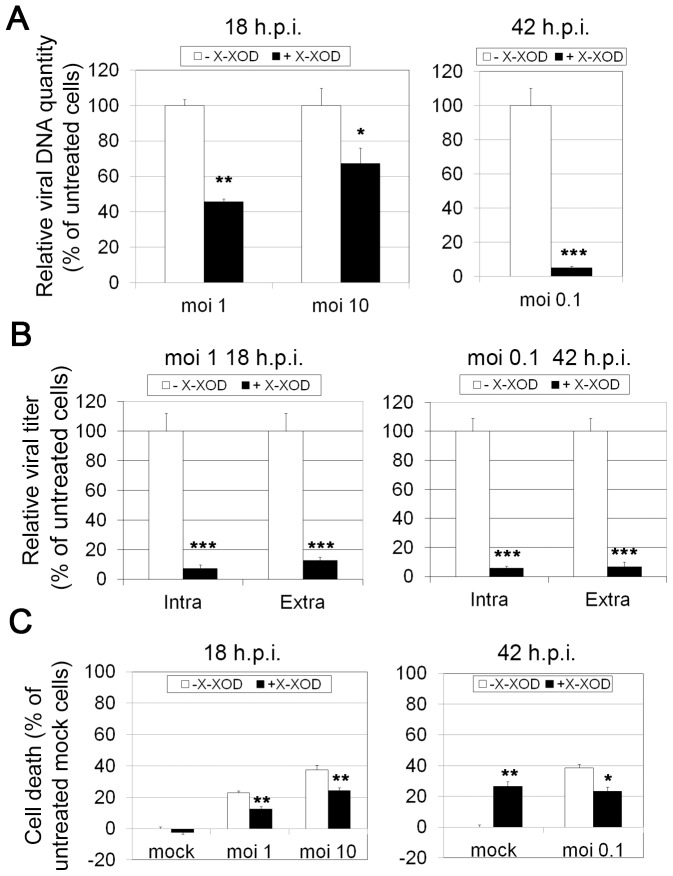
Figure 7. Oxidative stress reduces HSV-1 replication and increases cell viability of infected cells.
A) Quantification of viral DNA by real-time quantitative PCR in SK-N-MC cells simultaneously treated with X-XOD and infected with HSV-1 at a moi of 1 and 10 for 18 h or at a moi of 0.1 for 42 h. B) Intracellular (intra) and extracellular (extra) viral titres were determined by plaque assays in SK-N-MC cells infected under the same conditions as in (A). In (A) and (B), the data represent the mean ± SEM of five experiments performed in triplicate and are expressed as a percentage with respect to untreated cells (- X-XOD) (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001). C) The cell viability of mock and HSV-1-infected SK-N-MC cells exposed to X-XOD was monitored using the MTT reduction assay. Cells were infected with HSV-1 at a moi of 1 and 10 for 18 h or at a moi of 0.1 for 42 h. Values are expressed relative to the optical density of untreated mock-infected cells. The data shown represent the mean ± SEM for four independent experiments performed in triplicate (*p<0.05; **p<0.01).