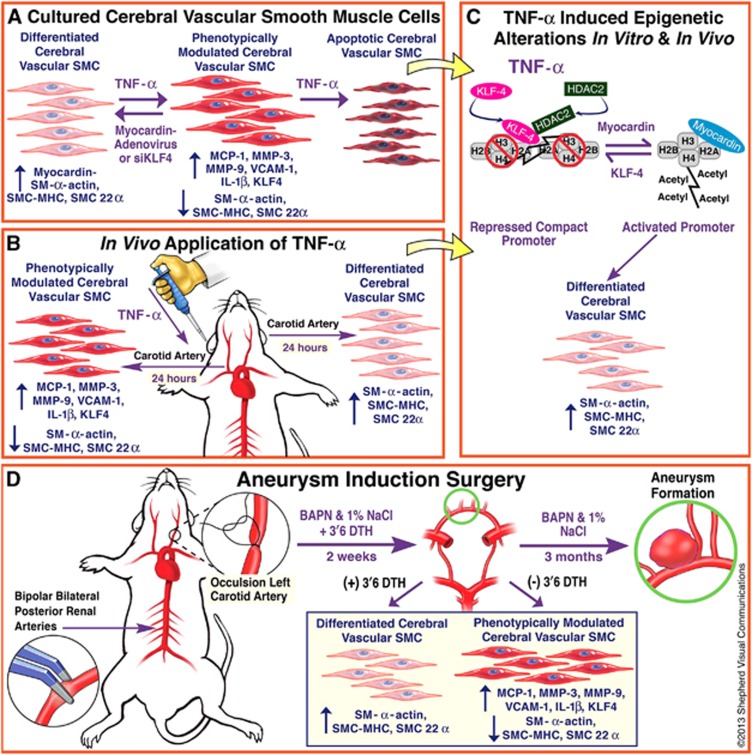
Figure 1.
Time-line of experiments. (A) Cerebral blood vessels (circle of Willis) from rats were harvested for cerebral vascular smooth muscle cell (SMC) culture and treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) for quantitative polymerase chain reaction, western blot, evaluation of apoptosis, and assessment after adenovirus promoter transfection. (B) After experiments in vitro, experiments were carried out after application of pluronic gel containing TNF-α to the adventitial surface of rat carotid arteries to directly evaluate phenotypic modulation in vivo. (C) Additionally, chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were carried out to determine epigenetic alterations in vitro and in vivo. (D) Subsequently, the role of TNF-α and the TNF-α inhibitor 3,6′-dithiothalidomide was assessed early on in an established rodent cerebral aneurysm model induced by hypertension and hemodynamic stress. BAPN, β-aminopropionitrile; SMC-MHC, smooth muscle cell myosine heavy chain.