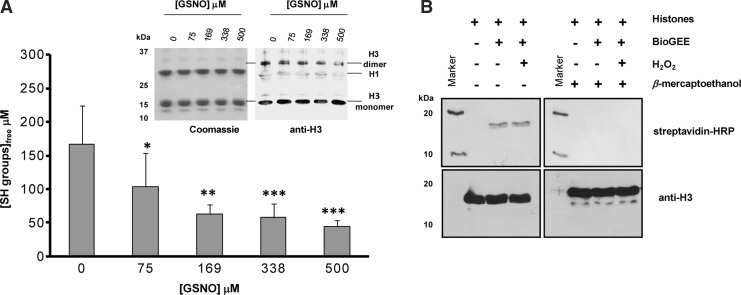
FIG. 1.
Chemical analysis of cysteine reactivity in histone H3. The number of free cysteine residues decreases with increasing concentrations of GSNO without dimer formation. (A) Titration of calf thymus histones with different concentrations of GSNO to detect free cysteine residues in histone H3. Detection of free cysteine residues was performed using DTNB, absorbance of TNB product was recorded at 420 nm. Results are expressed as means±standard deviation (SD) of five independent experiments. The statistical significance is expressed as: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.005 versus 0 μM GSNO. Inset: Immunoblot to evaluate monomeric and dimeric histone H3 from calf thymus after incubation with different amounts of GSNO (see A) using nonreducing conditions. (B) Immunoblot analysis of BioGEE treated core histone proteins from calf thymus using HRP-streptavidin (top) and anti-H3 antibodies (bottom). The experiments were carried out under nonreducing (left) and reducing (right) conditions, as indicated by the absence or presence of β-mercaptoethanol. BioGEE, biotinylated glutathione ethyl ester; DTNB, 5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid); GSNO, S-nitrosoglutathione; TNB, 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoic acid.