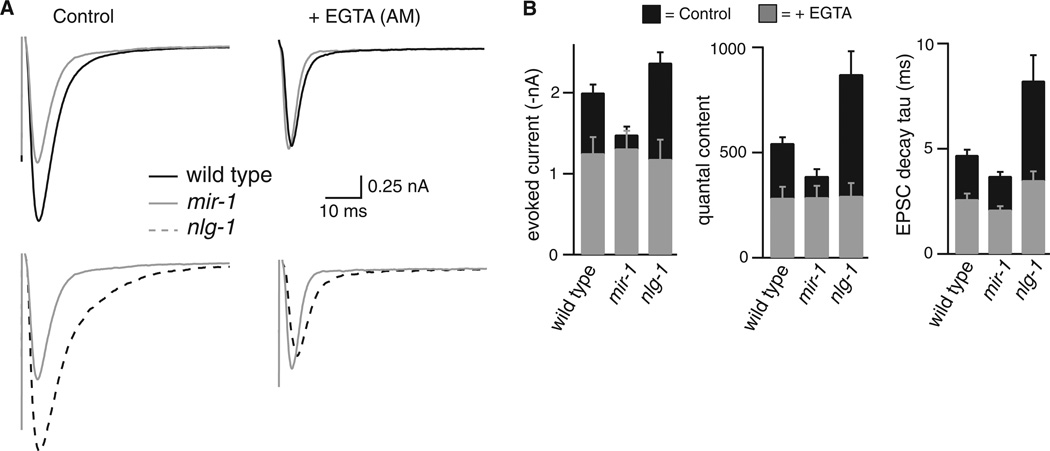
Figure 3. The effects of the retrograde signal on evoked responses are eliminated by EGTA.
(A) Averaged evoked responses are compared for wild type, mir-1, and nlg-1 mutants with and without EGTA-AM treatment. (B) Summary data are shown comparing evoked EPSC amplitude, decay kinetics, and quantal content. The numbers of animals analyzed were: wild type (14 control, 12 + EGTA); mir-1 (25 control, 11 + EGTA); and nlg-1 (13 control, 8 + EGTA). Error bars indicate SEM. The amplitude, quantal content, and decay kinetics of evoked EPSCs were not significantly different in EGTA treated wild type, mir-1, and nlg-1 animals: amplitude (WT vs. mir-1, p = 0.976; WT vs. nlg-1, p = 0.972); quantal content (WT vs. mir-1, p = 0.999; WT vs. nlg-1, p = 0.993); and decay tau (WT vs. mir-1, p = 0.321; WT vs. nlg-1, p = 0.118).