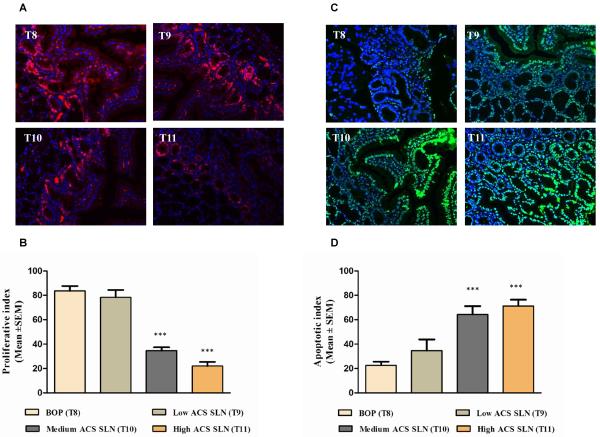
Figure 5.
Effect of ACS chemopreventive regimen on tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis. Immunohistochemical analysis and TUNEL assay was performed on paraffin-embedded and micro-sectioned hamster pancreatic tissues as described in methods section. (A) Representative figures showing effect of modified ACS SLN combination on PCNA expression in pancreatic lesions. (B) A significant decrease in the PCNA expression was observed in modified ACS treatment groups (T9–T11) compared to BOP (N-nitrosobis (2-oxopropyl) amine) carcinogen control (T8) group. (C) Representative figures showing effect of modified ACS SLN combination on apoptosis in pancreatic lesions. (D) A dose-dependent increase in the apoptosis was observed in ACS SLN treated groups (T9-T11) compared to the BOP carcinogen control (T8) group. All the pictures were taken at 200X magnification. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post hoc analysis. *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001 represents statistical significance between BOP carcinogen and ACS treatment.