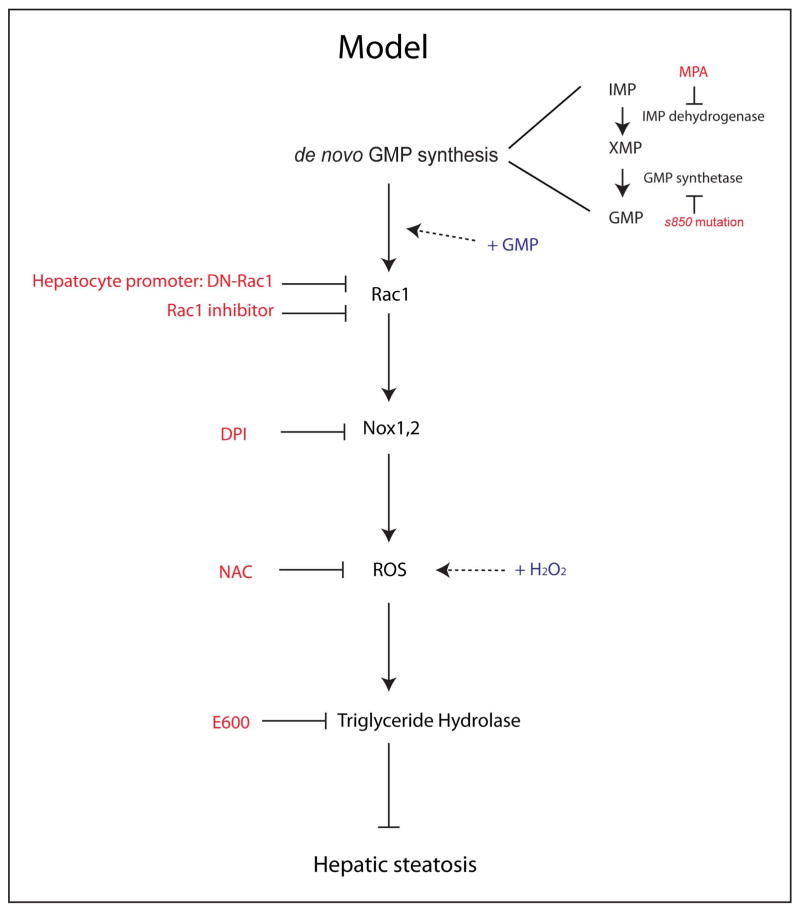
Figure 6.
Schematic model of ROS mediated liver protection from hepatic steatosis. Inhibiting de novo GMP synthesis by MPA-treatment or the GMP synthetases850 mutation induced hepatic steatosis. Supplying GMP rescued the hepatic steatosis phenotype in GMP synthetases850 mutant larva. De novo GMP synthesis influenced the activation of Rac1 and inhibiting Rac1 activity in hepatocytes by overexpressing dominant negative Rac1 (DN-Rac1) also induced hepatic steatosis. Rac1 regulates the activity of NADPH oxidases (Nox1, 2) and inhibiting NADPH oxidases mediated ROS production by DPI or quenching ROS by N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) also induced hepatic steatosis. Supplying hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) rescued the hepatic steatosis phenotype in GMP synthetases850 mutant, Rac1 inhibitor-treated, and DN-Rac1 expressing larvae. ROS levels influenced triglyceride hydrolase gene expression. The small molecule inhibitor for Triglyceride hydrolase (E600) treatment also induced hepatic steatosis.