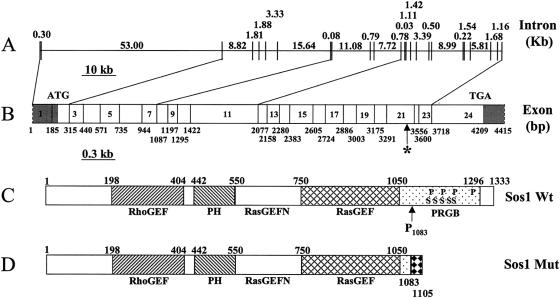
Figure 4.
Structure of the human SOS1 gene. A, Genomic organization of the SOS1 gene. The exons and introns are represented as vertical and horizontal lines, respectively. The sizes of each intron are shown in kb. B, cDNA structure of the SOS1 gene. The location of each exons are shown with the nucleotide numbers (bp). Since we did not determine the exact termini of the SOS1 cDNA, the N- and C-terminals are marked with dashed lines. The translation start and stop codon are labeled as ATG and TGA, respectively. The asterisk (*) marks the single-nucleotide (C) insertion between nucleotides 3248 and 3249. The 5′ and 3′ UTRs are shaded. C, Structure of the wild-type SOS1 protein. The location of each domain is marked by the amino acid numbers, with the initiation Met as amino acid 1. RhoGEF = guanine nucleotide-exchange factor for the Rho-Rac/cdc42-like GTPases region. PH = Pleckstrin homology domain. RasGEFN = guanine nucleotide-exchange factor for Ras-like GTPases; N-terminal motif. RasGEF = guanine nucleotide-exchange factor for Ras-like GTPases. PRGB = proline-rich Grbs-binding domain. In the PRGB domain, the location of the four proline-rich SH3 binding sites and the five phosphorylated serine residues are indicated by P and S, respectively. Codon 1083 (proline), where the single-nucleotide insertion occurs in HGF1, is indicated as P1083. D, Structure of the mutant SOS1 protein identified in patients with HGF. The 22–amino acid missense addition at the C-terminal end are marked with a black-diamond pattern.