Figure 1.
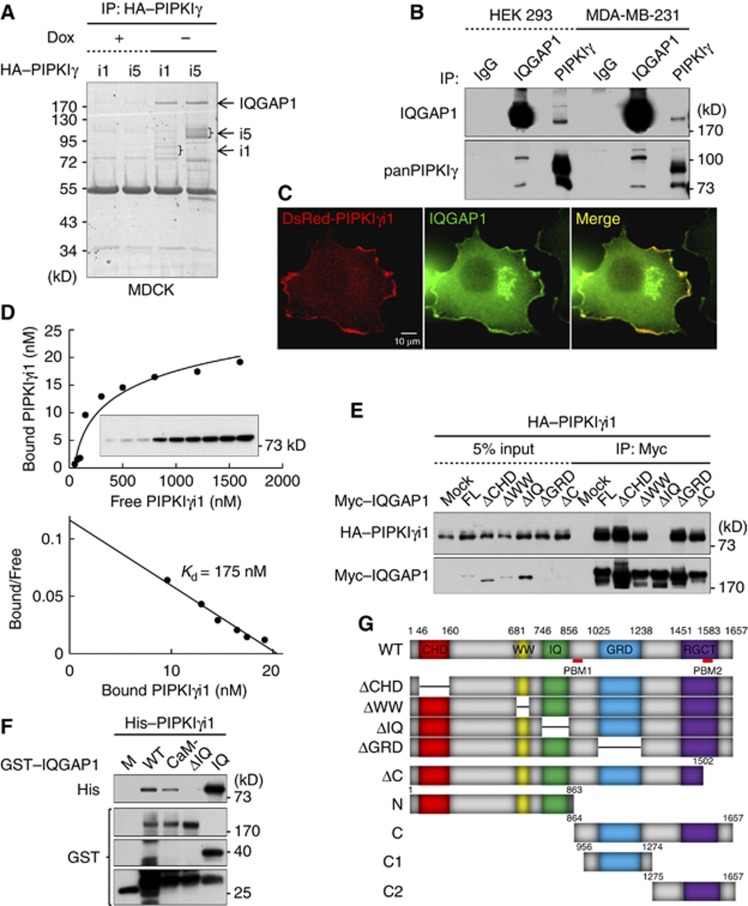
PIPKIγ interacts with the IQ motif of IQGAP1. (A) HA–PIPKIγi1 and i5 were expressed in tet-off MDCK cells, and an anti-HA antibody used to IP i1- and i5-containing complexes. Samples were resolved by SDS–PAGE and protein bands visualized by Coomassie staining. Dox, doxycycline. (B) PIPKIγ and IQGAP1 were separately IP’ed and association of the other protein examined by immunoblotting. IgG, isotype immunoglobulin control. (C) DsRed-PIPKIγi1 was transiently expressed in MCF-7 cells and endogenous IQGAP1 was immunostained. Cells were photographed under × 600 magnification. (D) GST-IQGAP1 (50 pM) was incubated with 5 to 1600, nM His–PIPKIγi1. Binding was detected by immunoblotting with an anti-His antibody (top). Kd was determined by standard Scatchard analysis (bottom). (E) Myc–IQGAP1 proteins were coexpressed with HA–PIPKIγi1 in HEK293 cells and proteins were IP’ed with an anti-Myc antibody. Associated PIPKIγi1 was analysed by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody. (F) Purified GST–IQGAP1 proteins were incubated with His–PIPKIγi1. The associated protein complex was examined by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Some degraded products of GST–IQGAP1 proteins were detected by immunoblotting with an anti-GST antibody. Data above are representative of at least four independent experiments. (G) Schematic representation of IQGAP1 domains and IQGAP1 constructs used for this study.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.