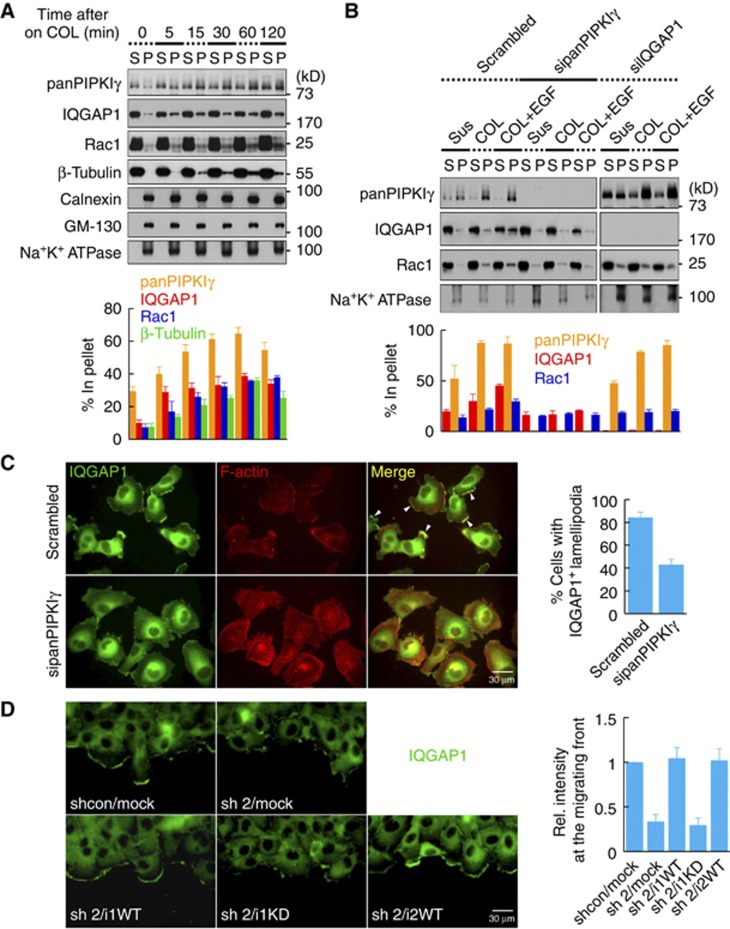
Figure 3.
PIPKIγ regulates IQGAP1 targeting to the leading edge membrane. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells maintained in suspension were plated on 10 ng/ml COL for the indicated times. Cells were lysed with a hypotonic buffer and the membrane fraction was separated from the cytosolic fraction by centrifugation. Then, 10 μg of each protein was resolved by SDS–PAGE and analysed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (top). The percentage of protein bound in the pellet relative to total (S+P) was calculated by quantifying the immunoblots (bottom). S, supernatant. P, pellet. (B) After transient knockdown with the indicated siRNA, cells were treated as in (A) in the presence or absence of 50 ng/ml EGF for 30 min. Cells were fractionated and analysed as above. (C) Serum-starved control or PIPKIγ knockdown cells were treated with 20 ng/ml EGF for 1 h. Cells were fixed and stained for IQGAP1 and F-actin. Cells were photographed at × 400 magnification. For quantification, at least 300 cells were counted. White arrowheads indicate IQGAP1-positive lamellipodia. Data are shown as mean±s.d. of three independent experiments. (D) Cells grown to confluence were wounded and fixed 3 h later, followed by immunostaining for IQGAP1. Cells were photographed at × 400 magnification. Intensity of fluorescent signal at the migrating front was measured from at least 10 different images of each condition and quantified using ImageJ software. Data are shown as mean±s.d. of three independent experiments. All the experiments described above were performed independently at least three times.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.