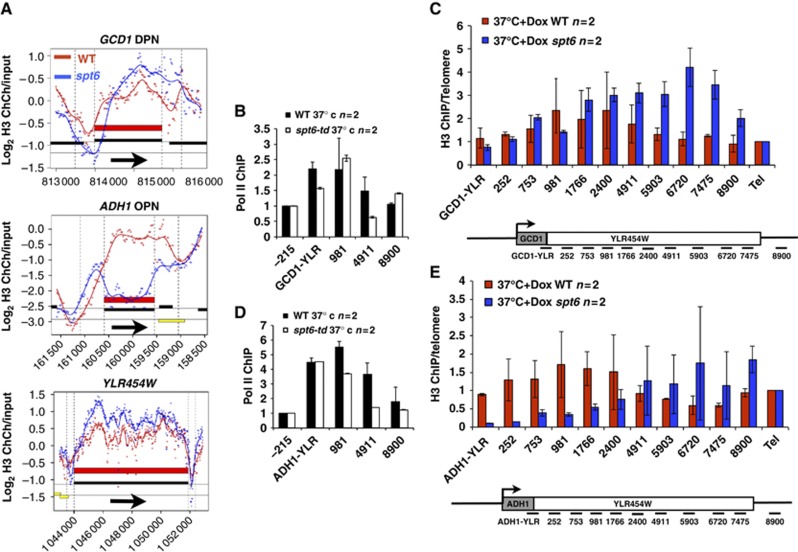
Figure 6.
Promoters can influence histone eviction/deposition within genes. (A) Histone H3 occupancy at GCD1, ADH1 and YLR454W in the spt6-td degron and WT strains (B, D) Pol II ChIP for the integrated GCD1- and ADH1-YLR454W genes in isogenic spt6-td strains DBY1327, 1330 and WT strains DBY1369, 1370 at 37°C+Dox quantified by Q-PCR. Signals were normalized to the YLR454W −215 flanking region. Means of PCRs from two biological replicates (two PCRs of each) and standard deviations (s.d.) are shown. Values refer to positions of the centre of the amplicons relative to the ATG of YLR454W. GCD1-YLR and ADH1-YLR are amplicons that span the boundary of these sequences at the 5′ end. (C, E) Histone H3 ChIP Q-PCR normalized to telomere VIR (TEL) for the GCD1- and ADH1-YLR454W genes in WT and spt6-td strains at 37°C+Dox. Maps of the amplicons are not to scale. Means of PCRs from two biological replicates (three PCRs of each) with s.d. are shown. Note the distinct effects of Spt6 inactivation on H3 occupancy within YLR454W driven by different promoters.