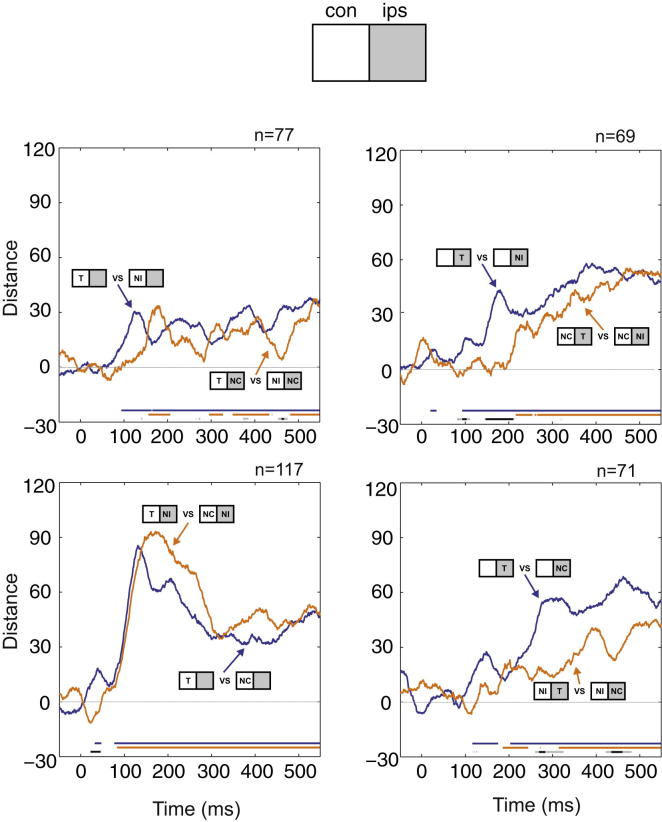
Figure 3.
Impairment of Neural Discrimination by Attentional Competition
Neural discrimination between critical T/N pairs presented either alone (blue) or accompanied by a nontarget in the opposite hemifield (orange), plotted as a function of time from choice stimulus onset. Discrimination is measured by Euclidean distance between activity vectors in a selected cell population, after subtraction of distance expected by chance (permutation correction; see Experimental Procedures). Discrimination significantly greater than zero (p < 0.05, blue and orange) and significant differences between single- and two-object displays (p < 0.05, light gray; p < 0.01, dark gray) are shown by lines at bottom. Top left: discrimination of Tcon versus NIcon, presented alone (blue) or accompanied by NCips (orange). Bottom left: discrimination of Tcon versus NCcon, presented alone (blue) or accompanied by NIips (orange). Top right: discrimination of Tips versus NIips, presented alone (blue) or accompanied by NCcon (orange). Bottom right: discrimination of Tips versus NCips, presented alone (blue) or accompanied by NIcon (orange). n indicates number of cells in each analysis.