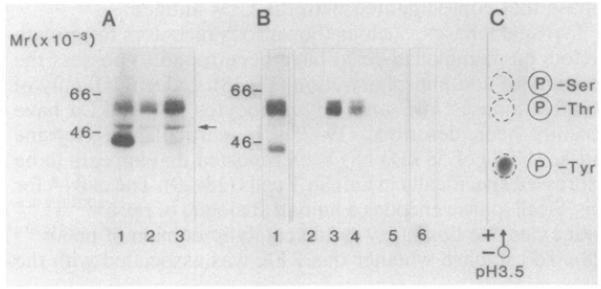
Fig. 2. NaDodSO4/PAGE analysis of the association between the CD4 and PTK antigens.
(A) Immunoprecipitates derived from peripheral blood lymphocytes that had been stimulated with Con A for 12 hr were labeled in a kinase assay (as described in Fig. 1). Enolase (1–2 μg; Sigma) was added as substrate to the beads before addition of the reaction mixture. Lanes: 1, anti-PTK antibody; 2, anti-CD4 antibody (12T4D11); 3, anti-CD4 antibody (19thy5D7). (B) Precipitation of the PTK polypeptide from CD4 immunoprecipitation. Anti-CD4 or anti-PTK precipitations were labeled by [γ-32P]ATP, denatured by boiling in either 1% NaDodSO4 (lanes 2, 3, 5, and 6) or 2% NaDodSO4 (lane 4), and diluted to 0.1% NaDodSO4 by a 1:10 or 1:20 dilution of lysis buffer, The denatured anti-CD4 immunoprecipitates were reprecipitated with the anti-PTK antibody (lanes 3 and 4). Conversely, the denatured anti-PTK immunoprecipitates were reprecipitated with a cocktail of anti-CD4 antibodies (12T4D11, 18T3A9, 19thy5D7) (lane 6). Lanes: 1, anti-CD4 pattern (19thy5D7) prior to denaturation; 2 and 5, anti-lF7 antibody; 3 and 4, anti-PTK antiserum; 6, anti-CD4 antibodies. (C) Phospho amino acid analysis of the polypeptides reprecipitated by the anti-PTK antiserum from immunoprecipitates formed by the anti-CD4 antibody. Polypeptides were eluted and subjected to phospho amino acid analysis as described (Fig. 1).