Figure 4.
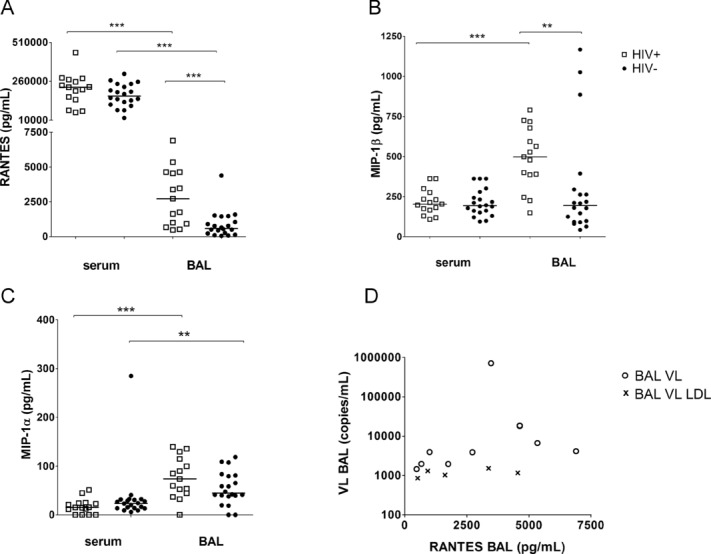
Chemokine concentration of RANTES, MIP-1β and MIP-1α in serum and BAL of HIV-1-infected (n = 15, open squares) or HIV-1-uninfected (n = 20, solid circles) persons. Chemokine concentration was measured by multiplex bead array; each symbol represents one sample, bars represent medians. (A) Differences of RANTES concentration between paired serum and BAL samples of HIV-1-infected (***p < 0.001) and HIV-1-uninfected persons were assessed by Wilcoxon signed rank test. The RANTES level in BAL in HIV-1-infected in comparison with HIV-1-uninfected (***p < 0.001) was calculated by Mann–Whitney U-test. (B) Difference of MIP-1β concentration between paired serum and BAL samples of HIV-1-infected participants (***p < 0.001) was assesses by Wilcoxon signed rank test. MIP-1β level in BAL was higher in HIV-1-infected versus HIV-1-uninfected persons (**p = 0.004, Mann–Whitney U-test). (C) Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to compare MIP-1α level in paired blood and BAL samples (***p < 0.001 in HIV-1-infected, **p = 0.01 in HIV-1-uninfected persons). (D) Correlation between RANTES concentration in BAL and viral load (VL) in BAL were assessed by Spearman (ρ = 0.635, p = 0.011). Open circles, BAL VL; symbol ×, BAL VL LDL were set to a value of 19 copies/mL and normalised according to the urea method. Data shown are pooled data from experiments on 15 HIV-1-infected and 20 HIV-1-uninfected persons.
