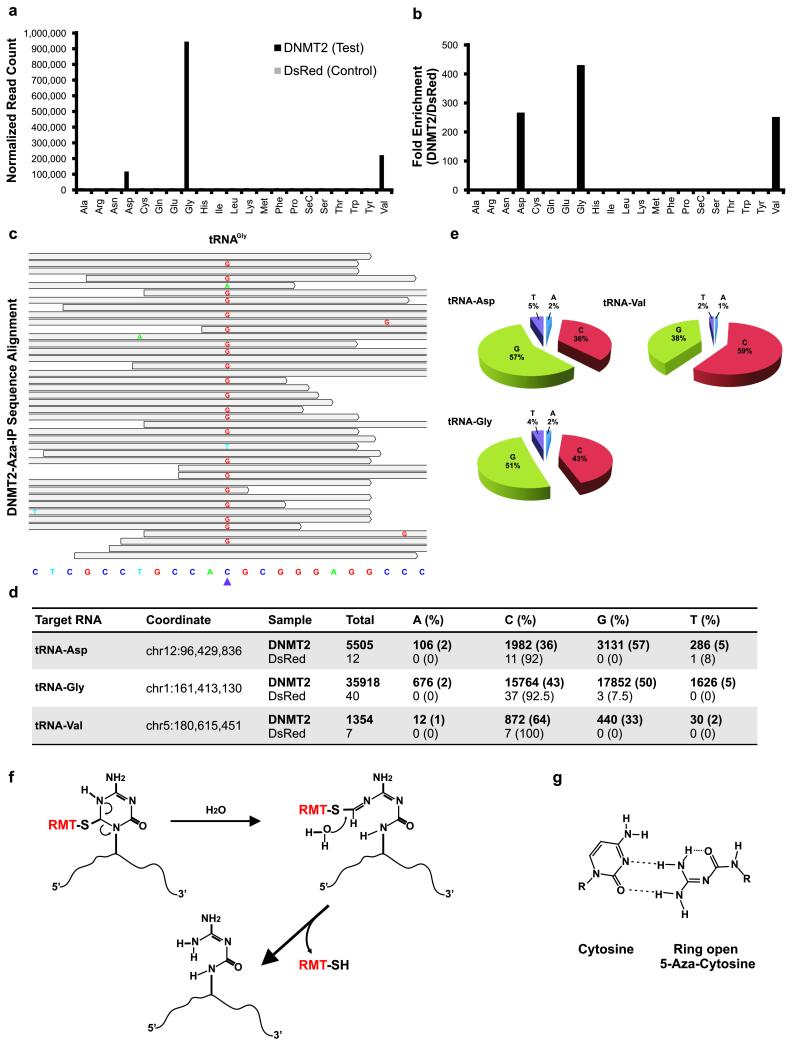
Figure 2.
Aza-IP analysis of DNMT2 RNA targets. (a) Graph depicts normalized reads mapping to each tRNA in the V5-DNMT2 (test) and V5-DsRed (control) datasets (one replicate of each shown). Each tRNA is designated by a three letter amino acid abbreviation. (b) Fold enrichment was calculated from the data shown in (a) by dividing the normalized RPKM (Reads Per Kilobase per Million mapped reads) values for each tRNA type in the V5-DNMT2 dataset by the values in the V5-DsRed dataset. (c) A representative snapshot from the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV, BROAD Inst.) browser depicting a subset of the sequencing reads mapped to a tRNAGly locus (chr1:161,413,119-161,413,141, human genome version 19 (hg19) bottom) at base pair resolution. The grey bars span the start/stop of individual sequencing reads mapped to the locus. The mismatched nucleotides are shown with colored letters and the matched nucleotides are hidden (grey). The purple arrowhead points to the tRNAGly C38 nucleotide (chr1:161,413,130). (d) Summary of the base distribution at the known DNMT2 target sites in tRNAAsp, tRNAGly and tRNAVal. The coordinate indicates the genomic location of the target cytosine in the human genome and the raw numbers are reported for both the V5-DNMT2 and V5-DsRed Aza-IP datasets. (e) Pie graphs showing the base distributions at the target nucleotide in the mapped reads. The numbers for the tRNAs are averaged over all of the annotated tRNA loci of same type in the human genome showing coverage over the target nucleotide (C38). (f) Schematic representation of the RMT-induced ring opening and RMT-RNA dissociation model. This model was proposed by Jackson-Grusby et al.25 for mammalian DNA cytosine methyltransferases and is adapted here for RMTs. RMT covalent linkage to the C6 position of 5-aza-C induces the rearrangement and ring opening and results in dissociation of the RMT from the target RNA molecule. (g) Base-pairing behavior of ring-open 5-aza-C. The ring-open 5-aza-C prefers to pair with cytosine and is therefore read as guanosine after RT-PCR and sequencing.