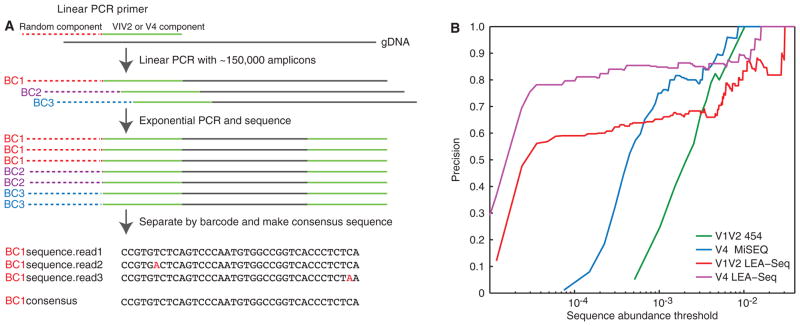
Fig. 1. Multiplex bacterial 16S rRNA gene sequencing using LEA-Seq; comparison with previous methods using mock communities composed of sequenced gut bacterial species.
(A) Schematic of how the LEA-Seq method is used to redundantly sequence PCR amplicons from a set of linear PCR template extensions of bacterial 16S rDNA. This approach results in amplicon sequences with a higher precision than standard amplicon sequencing at lower abundance thresholds. (B) Performance of 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing methods assayed as the precision obtained for different sequence abundance thresholds. Standard methods for amplicon sequencing using the 454 pyrosequencer and the Illumina MiSeq instrument exhibit increased precision as less abundant reads are filtered out. By redundantly sequencing each amplicon with LEA-Seq, the precision of amplicon sequencing is increased at lower abundance thresholds for both the V1V2 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene (compare red and blue lines) and the V4 region (compare magenta and blue lines), thereby enabling detection of lower-abundance bacterial taxa at high precision.