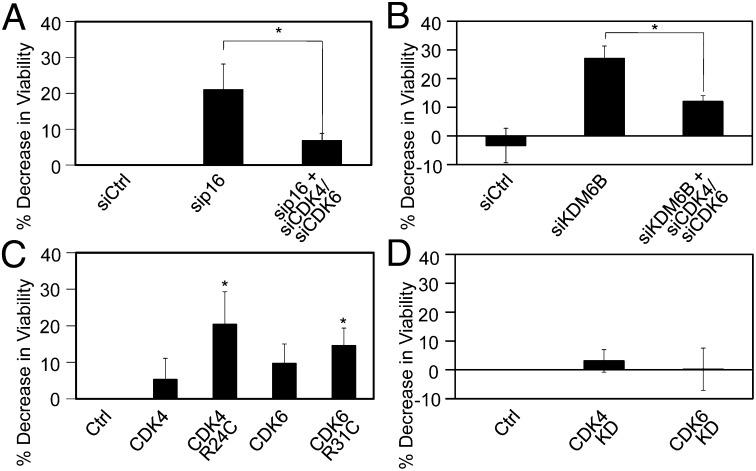
Fig. 6.
Cell death caused by p16INK4A depletion in p16INK4A-addicted cells is dependent on CDK4 and CDK6. (A) p16INK4A or p16INK4A, together with CDK4 and CDK6, were depleted in U2OS-tet on cells with doxycycline-inducible expression of HPV16 E7 by transfection with p16INK4A, CDK4-, or CDK6-specific siRNA duplexes. Transfection of the nontargeting siRNA pool was used as a control (siCtrl). (B) KDM6B or KDM6B in combination with CDK4 and CDK6 were depleted in U2OS-tet on cells with doxycycline-inducible expression of HPV16 E7 by transfection with KDM6B, CDK4-, or CDK6-specific siRNA duplexes. Transfection of a nontargeting siRNA pool was used as a control (siCtrl). (C) U2OS-tet on cells with doxycycline-induced HPV16 E7 expression were transfected with CDK4, CDK6, and oncogenic CDK4 or CDK6 mutants that cannot be inhibited by p16INK4A (R24C and R31C, respectively). Cell viability was measured by AlamarBlue assay. Averages and SDs for three independent experiments are shown. (D) Kinase-defective CDK4 or CDK6 mutants were transfected into U2OS-tet on cells with doxycycline-induced HPV16 E7 expression and did do not affect viability. Averages and SDs for three independent experiments are shown. Statistically significant changes are indicated: *P < 0.05.