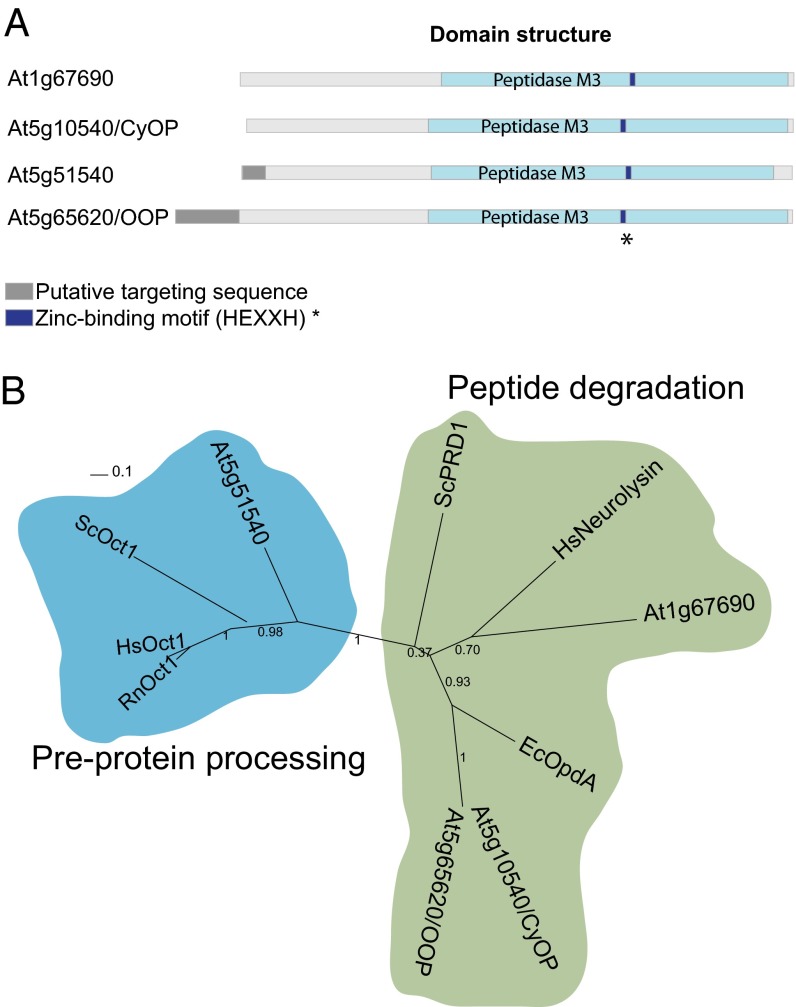
Fig. 1.
M3A peptidase homologs in A. thaliana. (A) Schematic representation of the structural and functional elements in the primary structure of M3A family peptidases. The putative targeting sequence (TargetP; www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/) is shown in gray, the peptidase M3 domain (Pfam; http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/) in light blue, and the Zn-binding motif in dark blue. (B) Phylogenetic tree of M3A peptidase homologs from several organisms, showing the two distinct groups. The tree was built based on the alignment shown in Fig. S1A. Sequences used for comparison were A. thaliana At1g67690 (F4HTQ1), At5g65620 (Q94:00 AM1), At5g10540 (Q949P2), and At5g51540 (F4KDA5); S. cerevisiae ScOct1 (P35999) and ScPRD1 (P25375); Homo sapiens HsOct1 (Q99797) and HsNeurolysin (Q9BYT8); Rattus norvegicus RnOct1 (Q01992); and E. coli EcOpdA (P27298). (The UniProt accession number for each homolog is given in parentheses.)