Fig. 6.
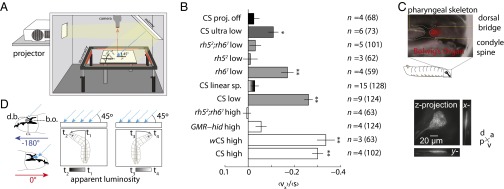
Directional lightscape navigation requires the Rh5 PRs of the BO. (A) Schematic of directional lightscape apparatus. Light rays are incident to larvae at 45°. (B) Navigational index (vx)/(s). Rejection of null hypothesis that dataset has same mean as projector-off dataset: *P < 0.01, **P < 0.0001, Welch two-tailed t test. For light intensities see Figs. S1 and S2. n = number experiments (number larvae). (C) The BO sits in a pigment cup formed by the cephalopharyngeal skeleton. (Upper) Fluorescence microscopy of GMR−RFP merged with bright-field microscopy. The white dotted line indicates the cephalopharyngeal skeleton. (Lower) Maximum intensity projections from 3D confocal microscopy of the BO in longGMR > CD8:: GFP larva. (D) Schematic of differential view angle of the BO conferred by cephalopharyngeal skeleton.
