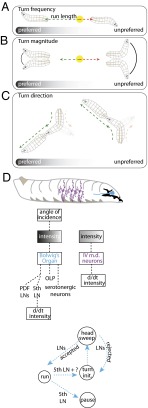
Fig. 9.
Models for the phototaxis navigational strategy and photosensory processing. (A) Larvae use temporal comparisons of light intensity during runs to modulate turn frequency. The gradient represents the light intensity. (B) Larvae make larger turns from the nonpreferred direction and smaller turns from the preferred direction. (C) Larvae use head-sweeps as probes to explore their local environment and to identify the preferred direction for successive runs. Turn direction bias is generated by asymmetrical acceptance of head-sweeps toward the preferred direction. (D) Model of larval photosensory processing based on temporal derivatives of lumonisoty (d/dt) as described in text.