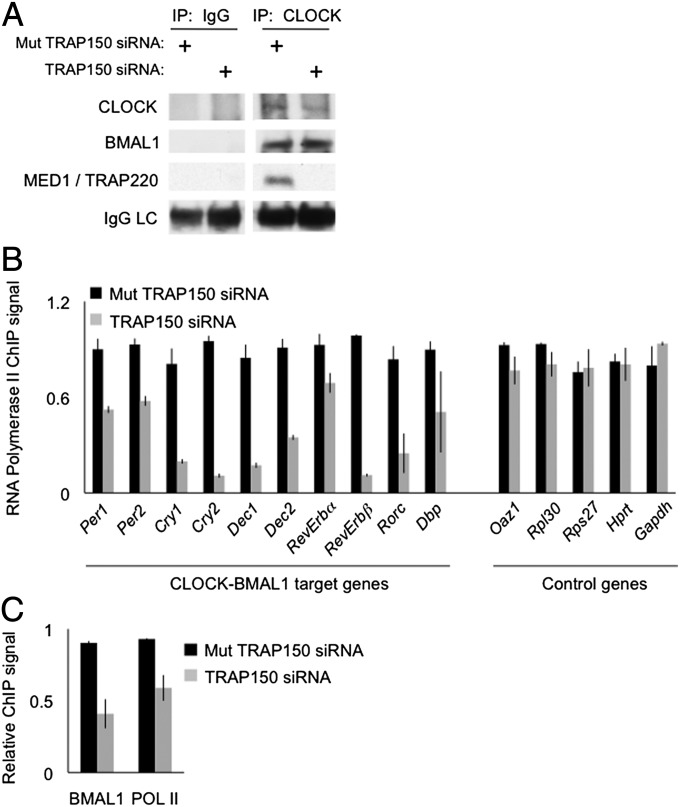
Fig. 5.
TRAP150 links CLOCK-BMAL1 to basic transcriptional machinery. (A) IgG control or CLOCK immunoprecipitations showing the effect of TRAP150 depletion on the association of CLOCK (or BMAL1) with the MED1/TRAP220 subunit of Mediator. Note that depletion of TRAP150 had no appreciable effect on the CLOCK-BMAL1 interaction. (B) ChIP assays showing the effect of TRAP150 depletion on the association of RNA polymerase II with E-box sites of CLOCK-BMAL1 circadian target genes or comparable sites of noncircadian control genes, as indicated. Association of RNA polymerase II with E-box sites could reflect direct binding nearby or cross-linking of CLOCK-BMAL1 at E-box to RNA polymerase II at or near transcriptional start site (with looping of intervening DNA). Shown are mean ± SEM of triplicate experiments. For each gene, signals were normalized to the highest value among the six measurements (triplicate control and triplicate TRAP150 depletion). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) ChIP assays showing the effect of TRAP150 depletion on BMAL1 binding or RNA polymerase II binding to the Trap150 gene E-box site, as indicated. Data analyzed as for panel B above.