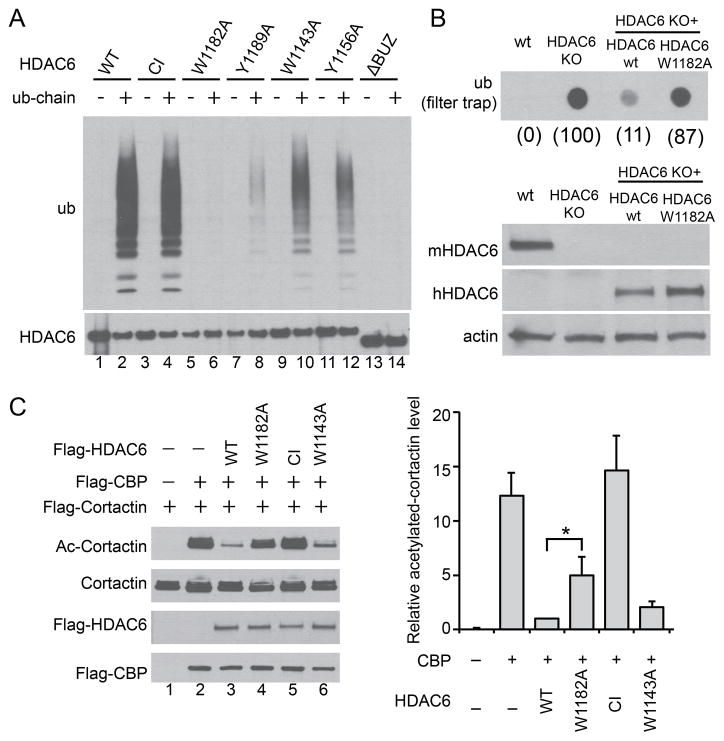
Figure 4. Free ubiquitin chains regulate HDAC6 activity.
(A) Immuno-purified FLAG-HDAC6 wild type (WT), H215A/H610A catalytic inactive (CI), and various point mutants were incubated with free ubiquitin chains as indicated. The bound fractions were detected by immuno-blotting with an ubiquitin antibody. (B) Upper panel, filter-trap analysis of SDS-insoluble ubiquitinated aggregates accumulated in wild-type (wt), HDAC6 KO, and KO MEFs stably expressing human wild type HDAC6 (wt) or W1182A mutant subject to 24h MG132 washout. The relative ubiquitin signal intensity was quantified and presented in parenthesis under each genotype where HDAC6 KO MEFs was set at 100. Lower panel, whole-cell extracts from indicated cell lines were immuno-blotted using antibodies for human HDAC6 (hHDAC6), mouse HDAC6 (mHDAC6) and actin. (C) Cortactin, the acetyltransferase CBP, and wild type or HDAC6 mutant plasmids were co-transfected into 293T cells as indicated. Cortactin was immuno-precipitated followed by immuno-blotting with an antibody for acetylated (Ac) cortactin or total cortactin. The relative cortactin-acetylation level (Ac-cortactin/cortactin) was quantified by scanning densitometry and presented in the right panel. Error bars indicate ± SD (n=3). The statistical significance was assessed using two-way ANOVA analysis with Dunnett’s test. *, p < 0.05. See also Figure S6.