Figure 1.
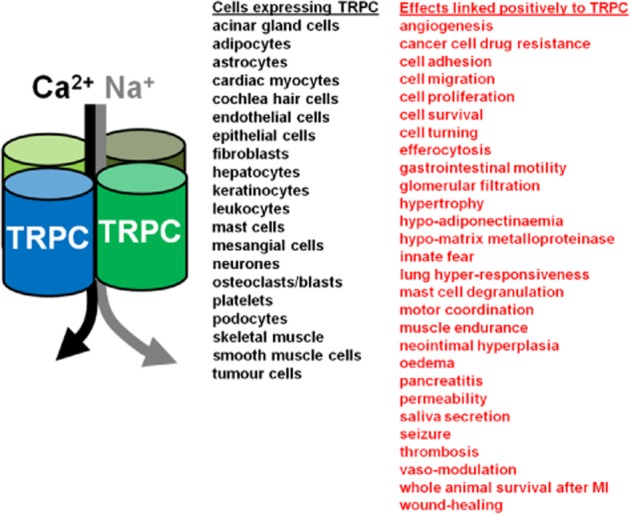
Expression and functions of TRPCs. On the left is a simple schematic diagram of a TRPC heteromer conferring influx of Ca2+ and Na+. In the middle is a list of the cell types that have been suggested to express TRPC mRNA or protein. On the right (in red) is a list of cell or whole tissue/body effects that have been suggested to be driven or potentiated by TRPC activity; in other words, if TRPC channels were to be inhibited, the opposite of the effect is predicted to occur (e.g. less pancreatitis). Example references for cell expression items: acinar gland cells (Liu et al., 2007); adipocytes (Sukumar et al., 2012); astrocytes (Shirakawa et al., 2010); cardiac myocytes (Eder and Molkentin, 2011); cochlea hair cells (Quick et al., 2012); endothelial cells (Ahmmed et al., 2004); epithelial cells (Kim et al., 2011); fibroblasts (Xu et al., 2008); hepatocytes (Rychkov and Barritt, 2011); keratinocytes (Cai et al., 2006); leukocytes (Yildirim et al., 2012); mast cells (Freichel et al., 2012); mesangial cells (Sours et al., 2006); neurones (Bollimuntha et al., 2011); osteoclasts/blasts (Abed et al., 2009); platelets (Ramanathan et al., 2012); podocytes (Dryer and Reiser, 2010); skeletal muscle (Gervasio et al., 2008); smooth muscle cells (Beech et al., 2004); and tumour cells (Thebault et al., 2006). Example references for effect items: angiogenesis (Yu et al., 2010); cancer cell drug resistance (Ma et al., 2012); cell adhesion (Smedlund et al., 2010); cell migration (Xu et al., 2006); cell proliferation (Sweeney et al., 2002); cell survival (Selvaraj et al., 2012); cell turning (Wang and Poo, 2005); efferocytosis (Tano et al., 2011); gastrointestinal motility (Tsvilovskyy et al., 2009); glomerular filtration (Dryer and Reiser, 2010); hypo-adiponectinaemia (Sukumar et al., 2012); hypo-matrix metalloproteinase (Xu et al., 2008); hypertrophy (cardiac) (Eder and Molkentin, 2011); innate fear (Riccio et al., 2009); lung hyper-responsiveness (Yildirim et al., 2012); mast cell degranulation (Ma et al., 2008); motor coordination (Trebak, 2010); muscle endurance (Zanou et al., 2010); neointimal hyperplasia (Kumar et al., 2006); oedema (Weissmann et al., 2012); permeability (Tiruppathi et al., 2002); pancreatitis (Kim et al., 2011); saliva secretion (Liu et al., 2007); seizure (Phelan et al., 2013); survival after MI (myocardial infarction) (Jung et al., 2011); thrombosis (Ramanathan et al., 2012); vaso-modulation (e.g. vasoconstriction) (Weissmann et al., 2006); and wound-healing (Davis et al., 2012).
