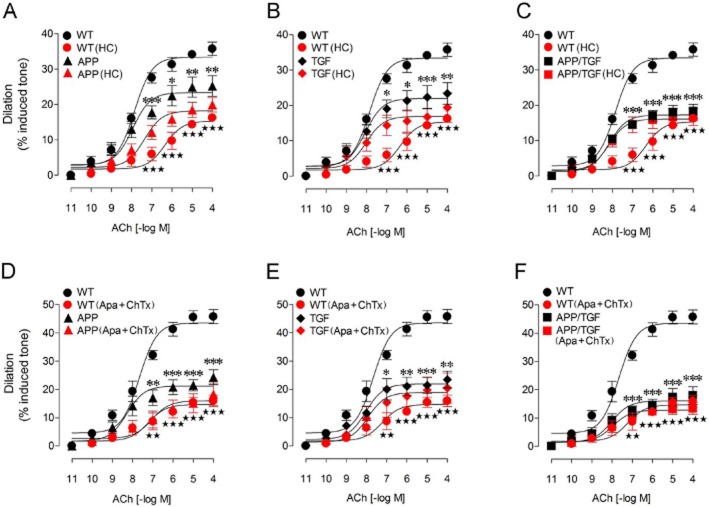
Figure 4.
HC, and combined apamin + ChTx reduced the ACh dilations in WT cerebral arteries, but not in vessels from APP, TGF and APP/TGF mice. Compared with WT vessels, the ACh-induced cerebrovascular dilations were significantly impaired in APP (A), TGF (B) and APP/TGF (C) mice. Treatments with HC (10−6 M) significantly reduced the ACh dilation in WT vessels, but had no or only modest effects in APP (A), TGF (B) or APP/TGF (C) arterial segments. Similar to HC, apamin (10−8 M) and ChTx (5 × 10−8 M) only affected vessels from WT mice, but not those from transgenic APP, TGF or APP/TGF mice (D–F). Only a small albeit significant decrease in the ACh pD2 value was observed in APP mice (D). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ⋆⋆ P < 0.01, ⋆⋆⋆ P < 0.001, when compared to untreated WT vessels by anova followed by a Newman–Keuls post hoc comparison test. Error bars represent SEM. n = 3–6 per group.