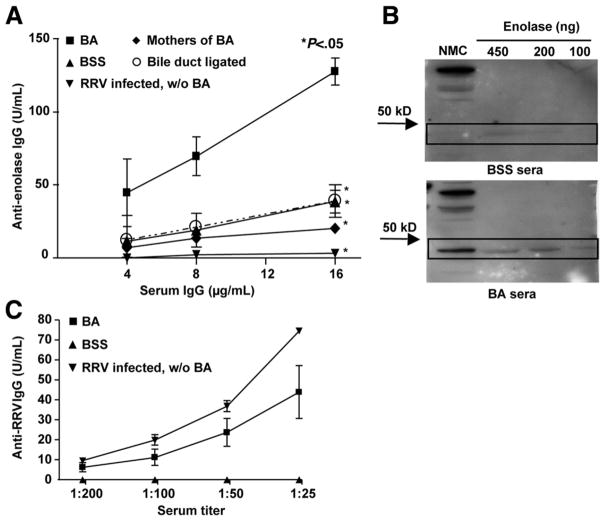
Figure 3.
Generation of anti-enolase antibodies within BA mice is dependent on both RRV infection and biliary obstruction. (A) ELISA: Plates were coated with purified enolase and incubated with sera followed by anti-IgG horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and substrate. Standard curves for anti-enolase were obtained and results shown as mean ± standard error of mean. Control mice included BSS; noncholestatic, RRV-infected siblings of BA (RRV infected, without [w/o] BA); mothers of BA; and bile duct ligated, chole-static adult mice. Significant differences in antibody levels were found between each control group and BA (*P < .05). (B) Western blot analysis: The NMC cytosolic fraction or purified enolase was incubated with sera, and IgG reactive to protein was visualized by chemiluminescence. (C) ELISA verification of RRV infection: Plates were coated with RRV and incubated with sera followed by anti-IgG HRP and substrate. Standard curves for anti-RRV were obtained and results shown as mean ± standard error of mean.