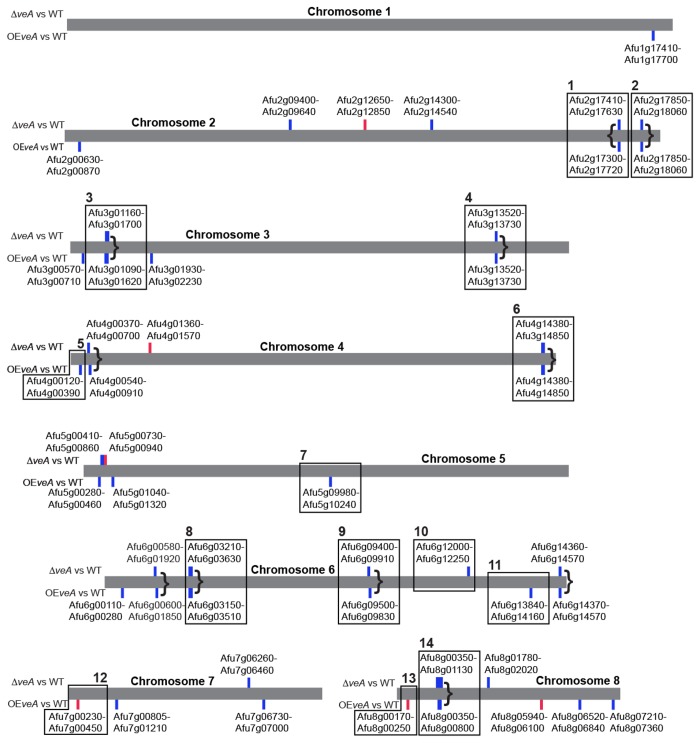
Figure 2. The genome-wide distribution of de novo identified gene clusters that appear to be regulated by veA.
De novo identification of gene clusters differentially regulated by the deletion versus wild-type (shown above each chromosome) and overexpression versus wild-type (shown below each chromosome) comparisons. Upregulated gene clusters are represented by red boxes and downregulated gene clusters are represented by blue boxes. Gene clusters identified in both comparisons whose boundaries overlap are denoted by bracket symbols. Previously reported secondary metabolism gene clusters [60,71] are boxed and numbered. 1: This cluster contains a conidial pigment biosynthesis cluster from Afu2g17530 – Afu2g17600 [82]; 2. This cluster contains the Fumigaclavine C cluster from Afu2g17960 – Afu2g18060 [83]; 3. Cluster of unknown function; 4. Cluster of unknown function; 5. This cluster contains an endocrocin secondary metabolism cluster from Afu4g00210 – Afu4g00230 [84]; 6. This cluster contains the pathway responsible for helvolic acid biosynthesis from Afu4g14770 – Afu4g14850 [85]; 7. Cluster of unknown function; 8. Cluster of unknown function; 9. This cluster contains the gliotoxin cluster from Afu6g09630 – Afu6g 09740 [86]; 10. This cluster contains the fumiquinazoline biosynthetic cluster from Afu6g12040 – Afu6g12110 [87]; 11. Cluster of unknown function; 12. Cluster of unknown function; 13. This cluster contains the fumitremorgin G cluster from Afu8g00260 – Afu8g00170 [76]; 14. This cluster contains the fumagillin gene cluster from Afu8g00370 – Afu8g00520 [53]; and the pseurotin A cluster from Afu8g00530 – Afu8g00570 [88].