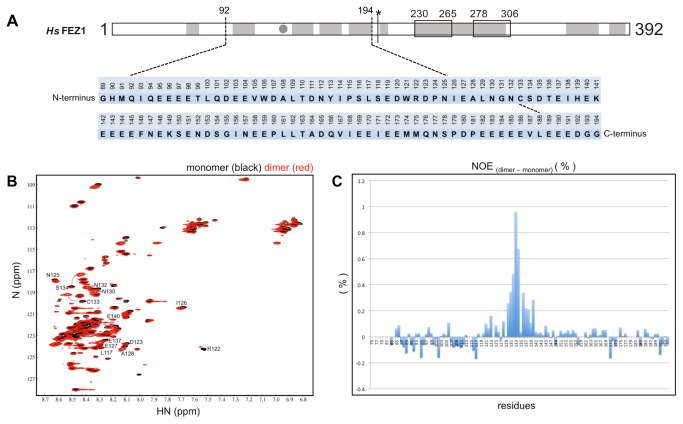
Figure 2. FEZ1 homodimerization involves few amino acids residues.
A) Amino acid sequence of human FEZ1 protein (92-194). The numbers indicate the position of each amino acid residue within the full-length sequence. The first three residues, unnumbered, are generated by the recombinant protein’s cleavage with TEV protease. B) 15N-HSQC FEZ1 (92-194) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectra. HSQC shows chemical shifts in reduced monomeric protein (black) and non-reduced dimeric protein (red). The spectrum was obtained in spectrometer 600 MHz. For the series of experiments, isotope 15N was introduced in minimal medium for growth of bacteria and induction of protein expression. C) steady-state heteronuclear NOE experiments with dimers and monomers. Heteronuclear NOEs intensities of the monomer were subtracted from those of the dimer, resulting in the differential pattern of relaxation corresponding to amino acids probably present in the region of homodimerization.