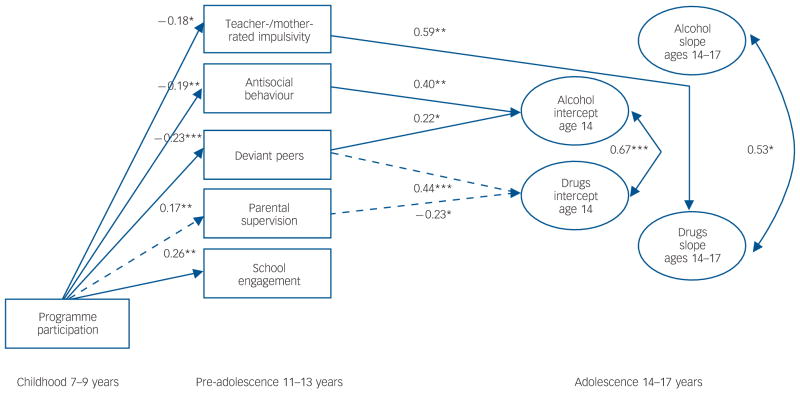
Fig. 3. Significant direct and indirect effects of the intervention on substance use outcomes.
Alcohol, alcohol use frequency; Drugs, number of drugs used. Only standardised coefficients are shown. Although not shown in the figure, the model included family adversity, pre-intervention disruptiveness and verbal IQ as covariates. Covariates and all variables assessed within the same developmental period (such as pre-adolescence and adolescence) were allowed to covary. Double-line arrows indicate significant mediated effects: the effect of programme participation on alcohol use at 14 years (intercept) was mediated by adolescent’s antisocial behaviours (ab = −0.028, 95% CI −0.05694 to −0.00614) and affiliation with deviant peers (ab = −0.018, 95% CI −0.04162 to −0.00077); the effect of programme participation on growth in number of drugs used from 14 to 17 years was mediated by impulsivity (ab = −0.013, 95% CI −0.02896 to −0.00033). Additional significant indirect, but not mediated, effects were found (indicated with broken double line arrows): programme participation on number of drugs used at 14 years (intercept) through affiliation with deviant peers (ab = −0.031, 95% CI −0.05812 to −0.01038) and poor parental supervision (ab = −0.012, 95% CI −0.02996 to −0.00012). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.