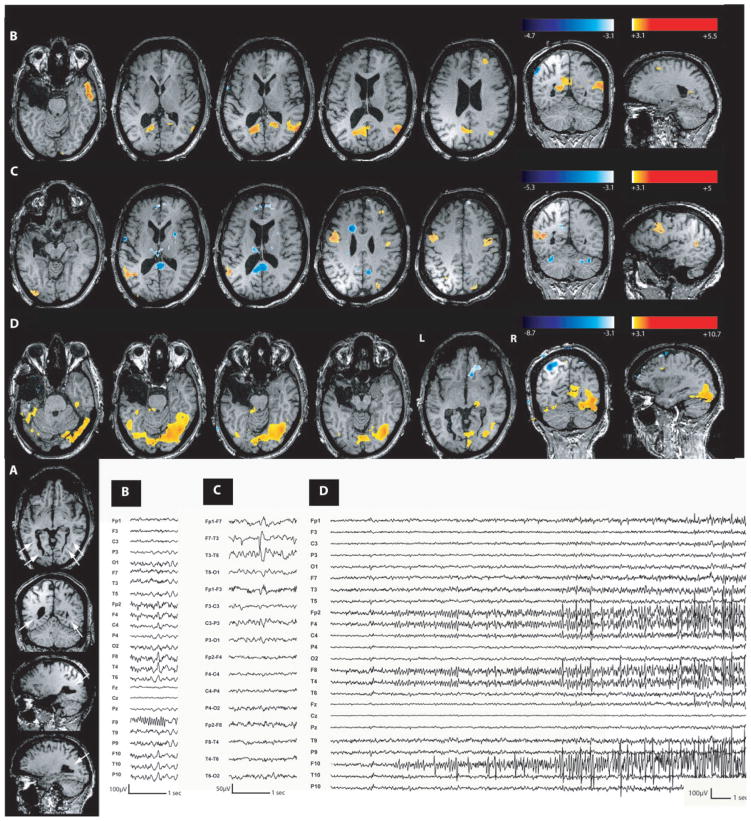
Fig. 3.
Nodular heterotopia (Patient 3). (A) Anatomical MRI showed a nodular heterotopia along both occipital horns (head of the white arrows). (B) Increased BOLD signal in the right temporal and parietal cortex and bilateral medial occipital gyrus during right temporal spikes. (C) Activation in the left temporoparietal cortex and bilateral middle frontal gyri during left temporal spikes. (D) Maximum activation during a single seizure in right occipitotemporal region. On EEG, the seizure started with a right centroparietotemporal fast activity. Nodular heterotopia were never involved during these different types of epileptic events.