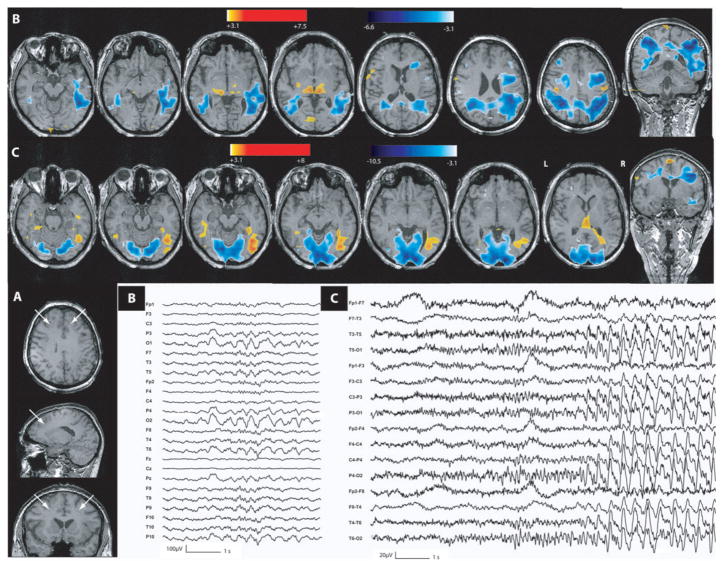
Fig. 8.
Band heterotopia (Patient 8). (A) Anatomical MRI showed a double cortex predominant in frontoparietal areas (head of white arrows). (B) BOLD decreased bilaterally in the heterotopic and normal cortices and increased in the thalami during short burst of temporoparietooccipital rhythmic slow waves. (C) During seizures, activation in the heterotopic and normal cortices mostly between the right occipitotemporal gyrus and the right inferior temporal lobe and in the left inferior temporal lobule. Ictal onset showed a rhythmic bilateral occipital and right temporoparietooccipital discharges. BOLD changes involved the normotopic and the heterotopic cortices during interictal and ictal epileptiform events. A deactivation was observed in the case of interictal events. These changes were predominant in the heterotopic cortex.