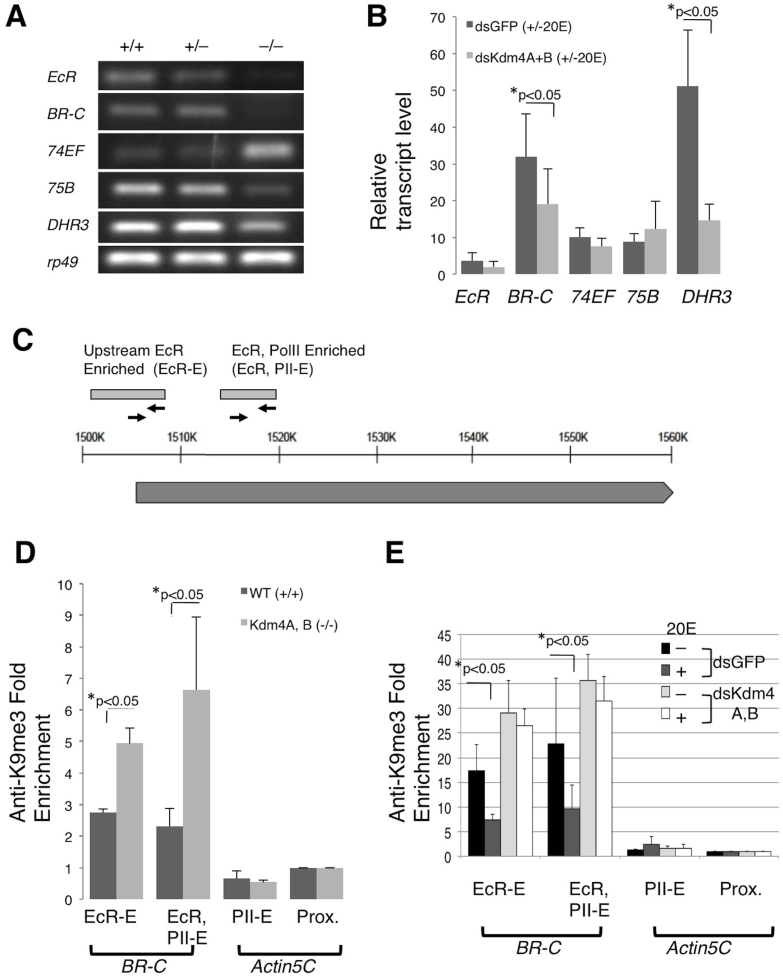
Figure 3. Kdm4A, B double homozygous mutants have reduced transcript levels of ecdysteroid pathway components.
(A) Wildtype (+/+), Kdm4AKG, BEY trans-heterozygous (+/−) or double homozygous (−/−) early second instar larvae were collected at the 51 to 54 hours AEL time point. Whole larvae were utilized for RT-PCR analysis to assess changes in transcript levels of EcR, BR-C, 74EF, 75B and DHR3 ecdysteroid puff genes, with rp49 serving as an internal control. (B) The ecdysteroid pathway was activated with 1 μM 20E treatment for 1 hour in S2 cells that had been treated with dsRNA specific for Kdm4A and Kdm4B, or for GFP (control). EcR, BR-C, 74EF, 75B and DHR3 transcript levels were subjected to quanitative-PCR analysis in triplicate. Transcript levels were normalized to rp49 and then expressed as fold change over those without 20 E treatment. Error bars represent standard deviation. (C) A schematic representation of the Broad genomic locus and primers used for ChIP. The light gray boxes represent the upstream EcR Responsive region36 and a region enriched for both EcR and PolII binding (ModEncode.org). The solid line represents genomic region, and the dark gray box BR-C transcript. The arrows represent primer pairs used for ChIP. (D) ChIP analysis was conducted with anti-H3K9me3 antibodies on wildtype and Kdm4AKG, BEY homozygous early second instar whole larvae staged at 51–54 AEL. At least three sets were analyzed. The Fold Enrichment method was used for calculation, with normalization to the actin5C proximal promoter primer sets. Error bars represent standard error. (E) S2 cells were treated with dsRNA specific for Kdm4A and Kdm4B, or for GFP (control), then with or without 1 μM of 20E for 1 hour, and were harvested and subjected to ChIP analysis with anti-H3K9me3 antibody in triplicates. The Fold Enrichment method was used for calculation, normalized to primer pairs amplifying the actin5C proximal promoter region. Error bars represent standard error.